Schizophrenia is a mental disorder that can be difficult to understand. There are five different subtypes of schizophrenia, each with its own unique set of symptoms and treatment methods. In this blog post, we will explore each of these subtypes in-depth and hear from experts about how they are treated. Furthermore, we will also provide resources for those who want to learn more about schizophrenia.
Contents
Understanding Schizophrenia
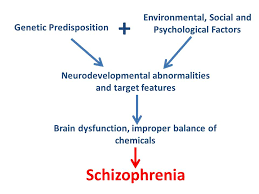
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder that is characterized by abnormal social behavior and failure to understand reality. Common symptoms of schizophrenia include hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking. Though the cause of schizophrenia is not fully understood, it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Symptoms of Schizophrenia

There are five different subtypes of schizophrenia, each with its own set of symptoms. The most common symptom of all types of schizophrenia is hallucinations, which are false or distorted perceptions of reality. Moreover, other common symptoms include delusions, disorganized thinking, and negative symptoms.
DSM And Its Criterion
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) is the standard classification of mental disorders used by mental health professionals in the United States. The DSM includes a wide variety of mental disorders, including schizophrenia.
The DSM-IV, published in 1994, listed eight criteria for diagnosing schizophrenia. These criteria have been revised in the DSM-V, published in 2013. The revisions were made to better reflect the current understanding of the disorder and to make the diagnosis more reliable.
The DSM-V (the most recent version of the DSM) defines five different subtypes of schizophrenia: paranoid type, disorganized type, catatonic type, undifferentiated type, and residual type. Each of these subtypes has its own set of symptoms that are used to diagnose the disorder.
Brain Activity During Schizophrenia
Brain activity during schizophrenia is abnormal. Moreover, studies have shown that people with schizophrenia have less activity in the frontal lobes of their brains. They are responsible for planning and decision-making. Thus, people with schizophrenia also have abnormal levels of dopamine, a chemical messenger in the brain.
Exploring Five Subtypes of Schizophrenia

Here is a closer look at the five different subtypes of schizophrenia:
Paranoid Type
The paranoid type of schizophrenia causes delusions and hallucinations. Delusions are false beliefs that are not based on reality. Hallucinations are false or distorted perceptions of reality. Thus, people with paranoid schizophrenia often believe that:
- people are out to get them,
- someone is watching them, or
- someone is following them
Disorganized Type
The disorganized type of schizophrenia shows a pattern of disorganized thinking and behavior. Morever, people with this type of schizophrenia may have:
- trouble speaking coherently,
- face constant confusion, and
- may act bizarrely or irrationally.
Catatonic Type
The catatonic type of schizophrenia comes with abnormal movement and behavior. Moreover, people with this type of schizophrenia may be:
- completely unresponsive, or
- they may have repetitive or purposeless movements.
Undifferentiated Type
The undifferentiated type of schizophrenia shows a mix of symptoms from all other types of schizophrenia. Moreover, people with this type of schizophrenia may have:
- delusions,
- hallucinations,
- disorganized thinking, and
- abnormal movement.
Residual Type
The residual type of schizophrenia comes with a decrease in symptoms from other types of schizophrenia. Moreover, people with this type of schizophrenia may have:
- fewer and less intense delusions,
- hallucinations, and disorganized thinking.
However, they may still have negative symptoms, such as social withdrawal and apathy.
Treating Each Subtype of Schizophrenia
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to treating schizophrenia. Eventually, the best treatment plan caters to an individual’s specific symptoms and needs. In general, treatment for schizophrenia typically includes the right mix of medication, psychotherapy, and support from family and friends.
Paranoid Type
Experts recommend a combination of medication and psychotherapy to treat paranoid schizophrenia. Moreover, antipsychotic medication is the most common type of medication that helps treat this type of schizophrenia. Psychotherapy can help people with this type of schizophrenia to understand and cope with their delusions and hallucinations.
Disorganized Type
A combination of medication and psychotherapy is a common treatment approach which experts say. Moreover, antipsychotic medication is the most common type of medication that helps control the symptoms of this type of schizophrenia. Psychotherapy can help people with this type of schizophrenia to understand and cope with their disorganized thinking and behavior.
Catatonic Type
Normally medication is the first line of defense to treat this subtype of schizophrenia. Moreover, antipsychotic medication is the most common type of medication that helps treat this type of schizophrenia. People with this type of schizophrenia may also need to be hospitalized for their safety.
Undifferentiated Type
A combination of medication and psychotherapy is what experts suggest to treat this subtype of schizophrenia. Moreover, antipsychotic medication is the most common type of medication that helps treat this type of schizophrenia. Psychotherapy can help people with this type of schizophrenia to understand and cope with their symptoms.
Residual Type
A combination of medication and psychotherapy is the treatment approach to control and manage residual type schizophrenia. Moreover, antipsychotic medication is the most common type of medication that helps treat this type of schizophrenia. Psychotherapy can help people with this type of schizophrenia to understand and cope with their symptoms.
Talking To a Professional
If you are feeling like you may be struggling with schizophrenia or if someone you know is exhibiting symptoms of schizophrenia, talking to a professional is the best step. A mental health professional can help make an accurate diagnosis, provide resources and treatment options, and connect you with support groups or other services. You can find a therapist through your insurance provider or by contacting a national mental health organization, such as the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI).
Therapies for Schizophrenia
There are a number of different types of therapies available for schizophrenia. The most common type of treatment is medication, which can help reduce or control symptoms. However, therapy is also an important part of treatment and can help people with schizophrenia to function better in their everyday lives. Some common therapies include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): This type of therapy helps people learn how to change the thoughts and behaviors that may be contributing to their symptoms.
- Family-focused therapy: This type of therapy helps families understand and support their loved ones with schizophrenia.
- Psychodynamic therapy: This type of therapy focuses on the relationship between a person’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
- Supportive psychotherapy: This type of therapy provides emotional support and can help people manage their symptoms.
Medications for Schizophrenia
There are a number of different medications available to treat schizophrenia. Each person’s medication needs may be different, so it is important to work with a doctor to find the medication that is right for you. Some of the most common types of medications used to treat schizophrenia include:
- Antipsychotics: These medications are used to control symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions.
- Atypical antipsychotics: These medications are newer than traditional antipsychotics and may cause fewer side effects.
- Antidepressants: These medications are used to treat symptoms of depression, which can often occur along with schizophrenia.
- Anti-anxiety medications: These medications are used to treat symptoms of anxiety, which can also occur along with schizophrenia.
Hearing From Experts
Now that we know the different types of schizophrenia and how professionals treat them, let’s hear from some experts.
“The most important thing for people to remember is that there is hope. Schizophrenia is a treatable illness, and recovery is possible.” -Dr. David M. Jacobi, MD
“People with schizophrenia need treatment, support, and understanding. With proper care, most people with schizophrenia can manage their symptoms and live productive lives.” -Dr. John M. Davis, MD
Case Study
John is a 20-year-old college student who was struggling with paranoid type schizophrenia. John’s delusions began shortly after he started college. And he soon became convinced that his roommates were trying to harm him. In addition, John’s hallucinations began a few months later. As a result, he began to see and hear things that weren’t there.
John was prescribed antipsychotic medication, which helped to reduce his delusions and hallucinations. In addition, he also began individual therapy, which helped him to cope with his paranoia and mistrust of others. Finally, John is now able to live a relatively normal life and is doing well in school. However, it became possible with timely intervention and the right treatment.
Resources
If you or someone you know is struggling with schizophrenia, there are resources available to help. For instance:
- The National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) offers support groups and educational resources for people with mental illness and their loved ones. NAMI also advocates for better access to mental health care.
- The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) provides resources and support for people with mental illnesses, including schizophrenia. SAMHSA also offers a national helpline that can connect you with local resources.
NOTE: If you’re in crisis, the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline is available 24/seven at 800-273-TALK (800-273-825).
Conclusion
Schizophrenia is a serious mental illness that can be debilitating. However, with treatment, many people with schizophrenia can lead normal, fulfilling lives. So, if you or someone you know is struggling with schizophrenia, there are resources available to help. Remember, you are not alone.
A Word From Therapy Mantra
Your mental health — Your psychological, emotional, and social well-being — has an impact on every aspect of your life. Positive mental health essentially allows you to effectively deal with life’s everyday challenges.
At TherapyMantra, we have a team of therapists who provide affordable online therapy to assist you with issues such as depression, anxiety, stress, workplace Issues, addiction, relationship, OCD, LGBTQ, and PTSD. You can book a free therapy or download our free Android or iOS app.


