In this resource guide, we will explore some of the most important aspects of neuroscience. We will also hear from experts in the field about their work and what they see as the future of neuroscience.
Contents
- 1 Understanding Neuroscience
- 2 Studying Neuroscience
- 3 Applying Neuroscience
- 4 Promoting Brain Health With Neuroscience
- 5 Treating Neurological Disorders Using Neuroscience
- 6 Learning About Neuroplasticity
- 7 Hearing From Experts
- 8 Predicting Future of Neuroscience
- 9 Reading Related Terminologies
- 10 Conclusion
- 11 A Word From Therapy Mantra
Understanding Neuroscience

Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system. It covers everything from the development of the brain to how individual brain cells work, and how they interact with each other. Neuroscience is a relatively new field, but it has already yielded a great deal of information about how our brains function.
Objective
One of the key goals of neuroscience is to understand how the brain develops. We know that the brain starts developing very early in life and that it continues to grow and change throughout our lives. The exact process by which the brain matures is still not completely understood, but scientists are making great strides in this area.
Neuroscientist
A neuroscientist is a scientist who studies the nervous system. Neuroscientists use a variety of techniques to study the brain and nervous system. These techniques include:
- Neuroanatomy, which is the study of the structure of the nervous system;
- Neurophysiology, which is the study of how the nervous system functions;
- Neurochemistry is the study of the chemical composition of the brain; and
- Behavioral neuroscience is the study of how the brain affects behavior.
Brush-up Basics
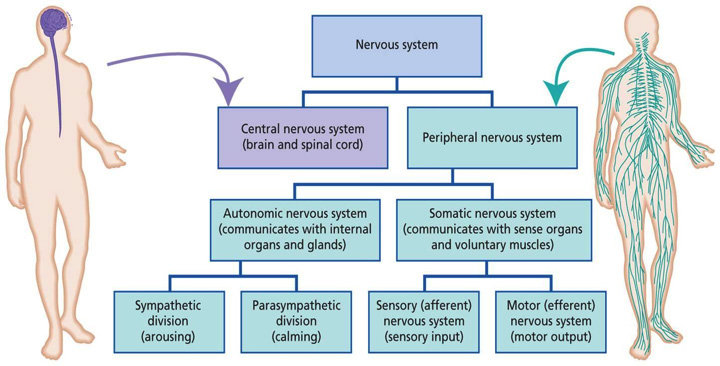
To understand neuroscience, it is first necessary to understand the nervous system. The nervous system is made up of two parts:
- the central nervous system (CNS), and
- the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
The CNS includes the brain and the spinal cord. The PNS consists of all of the nerves that branch off from the CNS and extend to the rest of the body. The nervous system is responsible for sending signals from the brain to the rest of the body. These signals can be electrical, chemical, or both.
Areas of Study In Neuroscience
When you study neuroscience, you are learning about the scientific study of the nervous system. This includes everything from the development of the brain to how individual brain cells work and interact with each other. For example:
Brain development: This area of research focuses on understanding how the brain develops from infancy through adulthood.
Then how brain cells work: This area of research focuses on understanding the workings of individual brain cells and how they interact with each other.
How the nervous system functions: This area of research focuses on understanding how the nervous system works as a whole.
Further, how brain activity is measured: This area of research focuses on developing ways to measure brain activity. This can be done through a variety of techniques, including:
- EEG
- MRI
- PET
Diagnosis and treatment of brain disorders: This area of research focuses on diagnosing and treating brain disorders. This includes disorders such as:
Neuroplasticity: This area of research focuses on the ability of the brain to change in response to experience.
Fields of Study In Neuroscience
There are many different areas of neuroscience that researchers can specialize in. Some of the most common are:
- Clinical neuroscience: This area of research deals with diagnosing and treating psychiatric disorders using neuroscientific methods.
- Behavioral neuroscience: This is the study of how the brain affects behavior.
- Cognitive neuroscience: This field investigates the relationship between the brain and cognitive processes such as memory, learning, and perception.
- Neurobiology: This area of study looks at the biological basis of behavior. It examines the structure and function of the nervous system at the cellular and molecular levels.
- Neuropsychology: This field investigates how the brain influences behavior and mental function. It examines how damage to different parts of the brain can lead to specific psychological problems.
NOTE: There are many different ways to study neuroscience. Some people may choose to focus on a specific area, such as cognitive neuroscience or neuropsychology. Others may study neuroscience at the cellular or molecular level. And still, others may focus on clinical applications of neuroscience, such as diagnosing and treating psychiatric disorders.
Neuroscience Vs. Cognitive Science
There is some overlap between neuroscience and cognitive science. However, there are also significant differences between the two fields.
- Cognitive science is more interested in understanding how we process information.
- Neuroscience is focused on understanding the physical structure and function of the brain.
History And Development
The field of neuroscience is relatively new. It was not until the late 19th century that scientists began to study the nervous system systematically. In 1864, a French doctor named Paul Broca discovered that a particular area of the brain is responsible for speech. This was a breakthrough in our understanding of how the brain works. Since then, neuroscience has grown rapidly. Today, there are thousands of scientists all over the world working to unlock the mysteries of the brain.
Studying Neuroscience
When you study neuroscience, you are learning about the scientific study of the nervous system. This includes everything from the development of the brain to how individual brain cells work and interact with each other.
How Brain Develops
The brain develops over many years. It starts to form during the embryonic stage, and it continues to grow and change until late in life.
During early development, the brain is very malleable. This means that it can be easily changed or molded by outside influences. As a person gets older, however, this ability to change decreases. This is why it is so important for children to have positive experiences during their formative years.
How Brain Cells Work
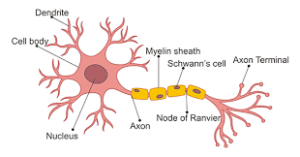
The brain is made up of cells called neurons. Neurons are electrically excitable cells that transmit information throughout the brain. They are responsible for everything from our thoughts and emotions to our movement and behavior.
Each neuron has three main parts:
- The cell body: It is the largest part of the neuron and contains the nucleus.
- The dendrites: They are thin, branched extensions that come out of the cell body. They receive signals from other neurons.
- The axon: It is a long, slender extension that carries information away from the neuron.
When a signal travels down an axon, it causes a tiny sac called a vesicle to release neurotransmitters into the synapse. The neurotransmitters then diffuse across the synapse and bind to receptors on the dendrite of the next neuron. This process allows information to be transmitted from one neuron to another.
How Brain Activity Is Measured
Brain activity can be measured in many different ways.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG): It is one of the most common methods to measure brain activity. This device measures the electrical activity of the brain. It is often used to diagnose epilepsy and sleep disorders.
- Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is another method of measuring brain activity. This technique uses magnetic fields to measure the tiny electrical currents that are produced by the brain. MEG can be used to study a variety of conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, and brain tumors.
- MRI: This is a common imaging technique that uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to create images of the inside of the body. MRI can be used to measure brain activity by measuring changes in blood flow.
- Positron emission tomography (PET): This is another imaging technique that uses radioactive substances to measure brain function. PET can be used to study a variety of conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease, addiction, and schizophrenia.
NOTE: No matter what area of neuroscience you choose to focus on, the most important thing is to learn how to think critically and ask questions. As a researcher in any field, you should always be questioning your results and looking for ways to improve your methods.
Applying Neuroscience
Neuroscience can be applied in many different ways. It can be used to diagnose and treat psychiatric disorders, promote brain health, and understand how the brain works.
Diagnosis of Common Psychotic Disorders
There are many different psychiatric disorders, and each one is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Brain imaging techniques, such as MRI and PET, can be used to diagnose these disorders. These techniques allow doctors to see how the brain is functioning. They can help to identify abnormalities in the brain that may be associated with psychiatric disorders. This information can then be used to develop treatment plans.
Mental Health Treatment and Brain
Mental health disorders are a common target for neuroscience research. Scientists are working to better understand how these disorders develop and how they can treat them effectively. In many cases, mental health disorders are an outcome of chemical imbalances in the brain. For example, depression bears a link to an imbalance of the neurotransmitter serotonin. By understanding the underlying causes of mental health disorders, scientists can develop new and better treatments.
Promoting Brain Health With Neuroscience

There is a lot that we still don’t know about the brain. However, we do know that there are things we can do to keep our brains healthy.
- Exercise is one of the best ways to promote brain health. Studies show that exercise increases cognitive function and protects against age-related decline. It also helps to reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias.
- Eating a healthy diet is also important for brain health. Eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and omega-three fatty acids bear a link to better cognitive function. Additionally, staying mentally active by doing things like puzzles and crosswords can help to keep the brain sharp.
- Finally, getting enough sleep is essential for brain health. Sleep helps to consolidate memories and supports learning and cognitive function.
These are just a few of the ways that neuroscience can help us promote brain health. By understanding how the brain works, we can develop better methods for keeping it healthy and functioning at its best.
Treating Neurological Disorders Using Neuroscience

One of the most exciting applications of neuroscience is its use in treating neurological disorders.
Many neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, are currently untreatable. However, scientists are working hard to find new treatments for these conditions.
One promising avenue of research is stem cell therapy. Stem cells are cells that can differentiate into other types of cells. Scientists are investigating whether stem cell therapy can be useful to treat neurological disorders.
Another area of research is neuroplasticity. Neuroplasticity is the ability of the brain to change in response to experience. Researchers are studying how neuroplasticity can help us treat conditions like stroke and spinal cord injury.
Treatments
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS): This is a treatment that uses magnets to stimulate the brain. TMS can help us treat conditions such as depression and anxiety.
Deep brain stimulation (DBS): This is a surgical treatment that involves implanting electrodes into the brain. DBS can help us treat conditions such as Parkinson’s disease and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS): This is a treatment that uses electrical impulses to stimulate the vagus nerve. VNS can help us treat conditions such as epilepsy and depression.
NOTE: These are just a few of the ways that neuroscience can help us treat neurological disorders. As our understanding of the brain grows, we will be able to develop more effective treatments for these conditions.
Learning About Neuroplasticity
The brain is constantly changing. This process is neuroplasticity. This is also known as brain plasticity and an antidote to Alzheimer’s disease.
Meaning
It means that the brain can change its structure and function in response to experience. This ability allows us to learn and remember new things, form new relationships, and adapt to changes in our environment.
Function
Neuroplasticity is also responsible for the development of neurological disorders. When something goes wrong with the brain, neuroplasticity can cause the brain to change its structure and function negatively.
However, neuroplasticity is not just a process that happens in times of distress. The brain can also change positively. This is called neuroplasticity-induced plasticity (NIP). NIP occurs when the brain changes in response to activities that are pleasurable or rewarding.
Tips To Boost Neuroplasticity
For example, learning a new skill or playing a musical instrument can cause the brain to change positively. This is because learning and playing music are activities that are fun and rewarding.
NIP can also help treat neurological disorders. By engaging in activities that are pleasurable or rewarding, we can help the brain to change positively. This can lead to improvements in symptoms and function.
Hearing From Experts
We spoke to two experts in the field of neuroscience about their work.
Dr. Wei Li
Dr. Wei Li is a research scientist at the McGovern Institute for Brain Research at MIT. Dr. Li studies how the brain processes information and how this impacts learning and memory.
“I want to understand how the brain works,” says Dr. Li. “How does it enable us to see, to hear, to smell, to taste, and to touch? How does it enable us to think, to reason, and to remember?”
Dr. Li has also an interest in how the brain changes as we learn new things. He studies a phenomenon known as neuroplasticity, which is the brain’s ability to adapt and change in response to new experiences.
“I want to understand how the brain changes as we learn new things,” says Dr. Li. “How do we store new memories? How do we forget old ones?”
Dr. Tara Swart
Dr. Tara Swart is a neuroscientist, doctor, and author. She is also the founder of The Neuroscience Academy, an online educational platform that offers courses and resources for people interested in learning about neuroscience.
“I want to help people understand how their brains work and how they can optimize their brain health,” says Dr. Swart. “I also want to show people that neuroscience is not just for scientists; it’s something that we can all benefit from.”
Dr. Swart says that many of her patients come to her with questions about how to improve their mental health.
“A lot of my patients are interested in brain health and want to know how they can protect their brains from damage,” says Dr. Swart. “I also see a lot of people who are struggling with mental health problems, such as anxiety and depression, and I help them to find the best treatment options for them.”
Resources
If you would like to learn more about neuroscience, here are some recommended resources:
- The Neuroscience Society: This is a great resource for all things neuroscience. They have a blog, news updates, and a forum where you can ask questions.
- The Dana Foundation: This is a non-profit organization that supports neuroscience research. They have a variety of resources, including articles, videos, and lectures.
- Neuroscientist TV: This is a great resource for anyone who wants to learn more about the people who work in neuroscience. It has interviews with prominent neuroscientists, as well as videos of their research.
Predicting Future of Neuroscience
The future of neuroscience is exciting. With new technologies, we can learn more about the brain than ever before. We are also developing new treatments for neurological disorders that are more effective and have fewer side effects.
In the future, we will continue to learn more about how the brain works and how we can optimize our brain health. We will also develop new treatments and therapies for neurological disorders that will improve the quality of life for patients.
The future of neuroscience is bright, and there is much to look forward to in the years to come.
Reading Related Terminologies
Below are some related terminologies that would be beneficial for individuals to be familiar with. This will help them in understanding the content of this blog post as well as future posts:
- Neurotransmitter: a chemical messenger that transmits signals between nerve cells
- Dopamine: a neurotransmitter involved in reward and pleasure, movement, and memory
- Serotonin: a neurotransmitter involved in mood, appetite, and sleep
- GABA: a neurotransmitter that inhibits nerve cells from firing
- Glutamate: a neurotransmitter that stimulates nerve cells to fire
- Stroke: a medical emergency in which the blood supply to the brain witnesses interruption, resulting in damage to the brain tissue
- Spinal cord injury: An injury to the spinal cord that can cause paralysis or loss of sensation
Conclusion
Neuroscience is a fascinating field of study with many potential applications. By better understanding the brain, we can develop new and effective treatments for conditions that affect the brain. Additionally, we can use neuroscience to promote brain health and prevent age-related decline. The future of neuroscience is bright, and there are many exciting things to come.
A Word From Therapy Mantra
Your mental health — Your psychological, emotional, and social well-being — has an impact on every aspect of your life. Positive mental health essentially allows you to effectively deal with life’s everyday challenges.
At TherapyMantra, we have a team of therapists who provide affordable online therapy to assist you with issues such as depression, anxiety, stress, workplace Issues, addiction, relationship, OCD, LGBTQ, and PTSD. You can book a free therapy or download our free Android or iOS app.