Compartmentalization is a psychological defense mechanism that allows people to mentally isolate one part of their lives from the others. It can be helpful in certain situations, but when it becomes excessive or starts to interfere with everyday life, it can be problematic. In this article, we will explore the different types and symptoms of compartmentalization, as well as the therapies available for those who need help. We will also look at how compartmentalization can affect relationships and work-life, and offer some tips for maintaining healthy boundaries.
Contents
Understanding Compartmentalization
Compartmentalization is a way of dealing with difficult or potentially harmful thoughts and emotions by keeping them separate from the rest of your life.
This can be helpful in some situations, such as when you need to focus on work or care for a loved one. However, excessive compartmentalization can lead to problems such as anxiety, depression, and isolation.
Is Compartmentalization a Mental Disorder
Compartmentalization is not a mental disorder, but it can be a symptom of one. If you find that you are excessively compartmentalizing your life, it may be worth talking to a professional about your symptoms.
Is Compartmentalization a Defense Mechanism
Compartmentalization is a defense mechanism that allows people to mentally isolate one part of their lives from the others. It can be helpful in certain situations, but when it becomes excessive or starts to interfere with everyday life, it can be problematic.
Compartmentalization Vs. Cognitive Dissonance
Compartmentalization and cognitive dissonance are two different ways of dealing with uncomfortable thoughts or emotions. Cognitive dissonance is the process of trying to rationalize contradictory beliefs, while compartmentalization is the act of mentally separating them.
Degrees of Compartmentalization
Compartmentalization can range from mild to severe.
- Mild compartmentalization is often helpful and doesn’t cause any problems.
- However, severe compartmentalization can lead to serious mental and physical health problems.
Types of Compartmentalization
There are four main types of compartmentalization:
Behavioral: This type of compartmentalization involves keeping different parts of your life separate from each other. For example, you may have a “work persona” and a “home persona” that are very different from each other.
Emotional: This type of compartmentalization involves keeping emotions separate from each other. For example, you may be able to feel happiness and sadness at the same time, but you don’t allow yourself to feel both emotions at once.
Cognitive: This type of compartmentalization involves keeping thoughts and emotions separate from each other. For example, you may know that you are angry with your boss, but you don’t allow yourself to feel the anger until after work.
Spatial: This type of compartmentalization involves keeping things separate in space. For example, you may have a desk for work and a desk for home, or you may keep your personal items in one room and your work items in another.
Symptoms of Compartmentalization
The symptoms of compartmentalization can vary depending on the type.
Cognitive symptoms may include:
- Disconnection from your emotions
- difficulty concentrating
- feeling numb or empty
- Difficulty making decisions
Emotional symptoms may include:
- Avoidance of certain emotions
- Feeling like you are not in control of your emotions
- Difficulty expressing emotions
Behavioral symptoms may include:
- Lead separate lives
- Have different sets of friends
- Behave differently in different situations
Spatial symptoms may include:
- Keeping work and personal items separate
- Having separate areas for work and home life
Causes of Compartmentalization
Many different factors can lead to compartmentalization. Some of the most common causes include:
Trauma: If you’ve experienced a traumatic event, you may start to compartmentalize as a way to protect yourself from reliving the trauma.
Stress: When people are under a lot of stress, they may find it easier to compartmentalize their lives to focus on one task at a time.
Abuse: If you’ve been a victim of abuse, you may start to compartmentalize as a way to deal with the pain and confusion.
Neglect: If you’ve been neglected, you may start to compartmentalize as a way to cope with the feelings of abandonment.
Poverty: If you’re living in poverty, you may start to compartmentalize as a way to deal with the stress and insecurity of your situation.
Negative Beliefs: People who have negative beliefs about themselves or the world around them may be more likely to compartmentalize their lives.
Prone Personality Types
Certain personality types are more prone to compartmentalization. These include:
Introverts: Introverts often compartmentalize as a way to protect themselves from the demands of the outside world.
Perfectionists: Perfectionists often compartmentalize as a way to control their environment and avoid making mistakes.
Workaholics: Workaholics often compartmentalize as a way to avoid dealing with their personal lives.
People pleasers: People pleasers often compartmentalize as a way to avoid conflict and please others.
Control freaks: Control freaks often compartmentalize as a way to feel in control of their lives.
Type-A personalities: Type-A personalities often compartmentalize as a way to stay on top of their lives and avoid feeling overwhelmed.
Avoidant Personality Disorder: People with this disorder may start to compartmentalize as a way to avoid intimacy and close relationships.
People with anxiety disorders: People with anxiety disorders may start to compartmentalize as a way to avoid triggering their anxiety.
People with depression: People with depression may start to compartmentalize as a way to avoid feeling overwhelmed by their emotions.
Professions That Involve Compartmentalization
Certain professions can increase your risk of developing compartmentalization.
Some of the most common professions include:
Military: The military often requires its members to compartmentalize their lives to follow orders and stay focused on the task at hand.
Law enforcement: Law enforcement officers often have to compartmentalize their personal and professional lives to maintain objectivity.
Medical professionals: Medical professionals often have to compartmentalize their personal and professional lives to maintain a professional distance.
Emergency responders: Emergency responders often have to compartmentalize their emotions to deal with traumatic situations.
Evaluating Compartmentalization

If you’re concerned that you may be dealing with compartmentalization, there are several things you can do to evaluate your situation.
Some of the most common evaluation tools include compartmentalization:
- Scale: This scale can help you to evaluate the severity of your compartmentalization.
- Test: This test can help you to determine if you’re at risk for developing compartmentalization.
- Checklist: This checklist can help you to identify the areas of your life that may be affected by compartmentalization.
The Next Step
Once you’ve evaluated your situation, it’s important to analyze the effects of compartmentalization.
Some of the things you may want to consider include:
- How well do you manage your time?
- Do you feel like you’re in control of your life?
- Are there areas of your life that are affected by compartmentalization?
- Do you feel like you’re living a double life?
- How does compartmentalization make you feel?
- Are there any benefits to compartmentalization?
Its Benefits
There are several benefits to compartmentalization. However, some of the most common benefits include:
Greater clarity: Compartmentalization can help you to clarify your thoughts and feelings, which can lead to better decisions.
Enhanced creativity: Compartmentalization can help you to come up with new ideas by allowing you to explore all aspects of a problem.
Increased focus and productivity: When you compartmentalize your life, you can focus on one task at a time and achieve more.
Improved decision making: Compartmentalization can help you to make better decisions by allowing you to consider all of the facts and avoid being swayed by emotions.
Its Risks

There are several risks associated with compartmentalization. However, some of the most common risks include:
Isolation: When you compartmentalize your life, you may isolate yourself from the people who care about you.
Loss of intimacy: When you compartmentalize your life, you may avoid close relationships and miss out on important connections.
Depression and burnout: Compartmentalization can lead to depression and burnout if you’re not able to balance your life.
Diminished ability to empathize: When you compartmentalize your life, you may have a difficult time empathizing with others.
Increased stress and anxiety: Compartmentalization can lead to increased stress and anxiety levels.
Difficulty expressing emotions: When you compartmentalize your life, you may have difficulty expressing your emotions.
Loss of touch with reality: When you compartmentalize your life, you may start to lose touch with reality and become disconnected from your emotions.
Maintaining Healthy Compartmentalization

Compartmentalization is a common coping mechanism that can help you manage stress and anxiety. However, it’s important to be aware of the risks associated with compartmentalization and take steps to maintain healthy levels of compartmentalization.
If you’re looking for ways to manage compartmentalization, several self-help tips and tools can help.
Self-help Tips
If you’re looking for self-help tips to manage compartmentalization, there are several options available. However, some of the most common tips include:
Create healthy boundaries: When you create healthy boundaries, you can separate your personal and professional life without isolating yourself.
Schedule time for yourself: When you schedule time for yourself, you can focus on your personal life without neglecting your professional life.
Set aside time to relax: When you set aside time to relax, you can reduce the amount of stress and anxiety you feel.
Talk to a therapist: When you talk to a therapist, you can learn more about how to manage compartmentalization and its effects.
Maintain a support network: When you have a supportive network, you can share your thoughts and feelings without feeling like you’re burdening others.
Self-help Tools
If you’re looking for self-help tools to manage compartmentalization, there are several options available. However, some of them are as follows:
Journaling: JournalWhen you write down your thoughts and feelings, you can better understand them and find ways to cope with them.
Mindfulness meditation: When you practice mindfulness meditation, you can focus on the present moment and let go of your thoughts and feelings.
NOTE: By understanding and managing compartmentalization, you can take steps to reduce its negative effects and live a healthier life.
Making Connections While Compartmentalizing

When you compartmentalize your life, you may feel like you’re missing out on important connections.
However, it’s possible to make connections while still maintaining healthy levels of compartmentalization.
There are several ways to make connections while compartmentalizing:
Reach out to people: When you reach out to people, you can build relationships and connect with others.
Join social groups: When you join social groups, you can meet new people and make connections.
Talk to friends and family: When you talk to friends and family, you can stay connected with them.
Take online classes: When you take online classes, you can meet new people and make connections.
Doing Multitasking While Compartmentalizing

It is possible to do multitask while compartmentalizing.
You can compartmentalize your life by separating different areas such as work, family, and friends.
- When you’re working, you can focus on your work and avoid thinking about your family or friends.
- Likewise, when you’re with your family or friends, you can focus on them and avoid thinking about work.
This allows you to maintain different parts of your life without feeling overwhelmed or stressed.
Can a compartmentalized mind see the big picture?
It is possible to have a compartmentalized mind and see the big picture. In fact, some people argue that this is necessary for effective decision-making. For example CEOs, etc.
NOTE: However, if you’re struggling with compartmentalization, it’s important to focus on healthy ways to manage your thoughts and emotions. This will help you to live a more balanced and fulfilling life.
Talking To Professional
If you’re struggling with the risks associated with compartmentalization, it’s important to talk to a professional. Furthermore, therapists can help you to understand how compartmentalization is affecting your life and find healthy ways to manage it.
Therapies
If self-help techniques aren’t enough, several therapies can help. However, some of them are as follows:
EMDR: Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) is a type of therapy that helps you to process traumatic memories.
Medication: If compartmentalization is causing severe depression or anxiety, medication may be recommended.
Interpersonal Psychotherapy: Interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) is a type of therapy that focuses on your relationships with others.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of therapy that helps you to identify and change unhealthy thoughts and behaviors.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy: Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is a type of cognitive-behavioral therapy that helps you to manage your emotions and relationships.
Case Study
John is a 33-year-old man who has been struggling with anxiety and depression for years. He’s tried several self-help techniques, but nothing has helped. John’s therapist recommends cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). After six months of CBT, John is able to manage his anxiety and depression.
Hearing From Experts
To get a better understanding of this defense mechanism, we reached out to several experts.
Here’s what they had to say:
“Compartmentalization is the process of separating thoughts, feelings, and experiences into specific parts of our lives.” – Dr. Lisa Firestone, licensed psychologist, and author “Compartmentalization can be a healthy way to deal with difficult emotions or experiences.” – Dr. Jill Weisenberg, licensed psychologist “Compartmentalization can lead to problems when it’s used as a way to avoid dealing with difficult emotions or experiences.”
– Dr. John Duffy, licensed clinical psychologist
Brain Activity
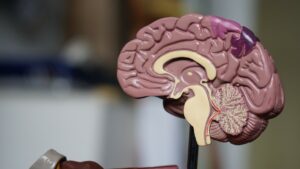
When we compartmentalize, our brain activity changes.
Here’s what researchers found:
- “The dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC) was more active when people with higher compartmentalization scores tried to keep their personal and professional lives separate.”
- “The dACC was also more active when people were successful in separating their personal and professional lives.”
- “Interestingly, the dACC was not as active when people with high compartmentalization scores tried to merge their personal and professional lives.”
– Dr. Cameron Anderson, associate professor of management at the University of California, Berkeley
Inference
Our research shows that the dACC is involved in this defense mechanism. This area of the brain is responsible for managing our thoughts and emotions. When we’re successful in separating our personal and professional lives, the dACC is more active.
Resources
If you’re struggling with compartmentalization, there are many resources available to help you. However, here are a few:
Books
- The Compartmentalized Mind: An Evolutionary Theory of Our Emotional Divide by Dr. Lisa Firestone
- Compartmentalize Your Life!: How to Organize, Delegate, and Maximize Your Time by Barbara Hemphill
Conclusion
Compartmentalization is a common defense mechanism. It can be helpful in some situations, but it can also lead to problems. Thus, if you’re struggling with it, don’t hesitate to seek help from a mental health professional. There are many resources available to help you understand and manage this condition.
A Word From Therapy Mantra
Your mental health — Your psychological, emotional, and social well-being — has an impact on every aspect of your life. Positive mental health essentially allows you to effectively deal with life’s everyday challenges.
At TherapyMantra, we have a team of therapists who provide affordable online therapy to assist you with issues such as depression, anxiety, stress, workplace Issues, addiction, relationship, OCD, LGBTQ, and PTSD. You can book a free therapy or download our free Android or iOS app.