It is possible to be completely in control of your actions, but not have any impulse control. This disorder can occur in people who are addicted to drugs or alcohol or suffer from some other psychological disorder. It may present itself in the form of addictive behavior, such as gambling or overeating.
Contents
- 1 What Is Impulse Control Disorder?
- 2 Symptoms
- 3 Signs In People With Psychological Disorders
- 4 Causes Of Impulse Control Disorder
- 5 Risk Factors Of Impulse Control Disorder
- 6 Impulse Control Disorder vs. ADHD
- 7 Treatment Options for Impulsivity
- 8 Importance of Controlling Impulses
- 9 Difference Between Impulses and Choices
- 10 Impulse Control Disorder Treatment
- 11 Disruptive control disorder
- 12 Conclusion
- 13 A Word From Therapy Mantra
What Is Impulse Control Disorder?

Impulse control disorder (ICD) is a psychiatric condition that can cause people to act on impulses that are harmful to themselves or others. This disorder can present itself in people who are addicted to drugs or alcohol, or who suffer from some other psychological disorder. Impulsive behavior can be extremely harmful, both to the individual with the disorder and to their loved ones.
Impulse Control Disorder (ICD) is a condition in which people have problems controlling their impulsive behaviors. Those who suffer from ICD might engage in dangerous activities impulsively, such as sex and violence, without thinking about the consequences of their actions. For example, someone with ICD may impulsively steal something because they want it right now. Similarly, someone with this condition may act violently on urges they perceive as threatening without considering its seriousness. People who struggle with this disorder often feel like they lack control over their impulses and actions even though they wish they could do so instead.
“Surprising numbers of Americans live with impulse-control disorders.”
Symptoms

Symptoms of impulse control disorder can vary depending on the person and the type of impulsive behavior exhibited. Some common symptoms include:
•Having difficulty resisting impulses
•Engaging in reckless or dangerous behaviors
•Difficulty inhibiting inappropriate behaviors
•Excessive spending or gambling
•Inability to control sexual or aggressive impulses
•Harm to oneself, such as substance abuse
People who suffer from impulse control disorder may not want to act impulsively. However, the force of the impulses they feel is overwhelming and outside their control. People with this condition might find it difficult to resist urges to lash out at others or take a chance on a big win even though they know they shouldn’t.
Signs In People With Psychological Disorders
People with addiction or other psychological disorders may exhibit impulsive behavior as a result of their condition. Impulse control disorder can be a symptom of addiction, as people may be unable to resist the impulse to use drugs or alcohol. Similarly, people with other psychological disorders may exhibit impulsive behaviors as a way to cope with their condition. For example, someone with bipolar disorder may impulsively spend money in an attempt to make themselves feel better.
Impulsive behavior can be very harmful to those with addiction or other psychological disorders. It can lead to further problems and complications in their lives. Additionally, it can be dangerous for others as well. Impulsive behavior can cause people to act on dangerous impulses without thinking about the consequences. This can be especially harmful in cases of sex and violence. People with psychological disorders may hurt themselves or others without thinking about the consequences of their actions.
Causes Of Impulse Control Disorder
There is no one definitive cause of impulse control disorder. Some possible causes include:
•Genetics – Some people may be more likely to develop ICD due to their genetic makeup.
•Environmental Factors – Certain environmental factors, such as a traumatic event or exposure to drugs or alcohol, can increase a person’s risk for developing ICD.
•Brain Chemistry – Changes in certain brain chemicals, such as serotonin and dopamine, can contribute to impulsivity.
• Mental Health Disorders – People with mental health disorders, such as bipolar disorder or schizophrenia, are more likely to experience impulsivity.
Risk Factors Of Impulse Control Disorder
Impulse control disorder can affect anyone, regardless of their age, sex, or race. However, there are some factors that may increase a person’s risk for developing ICD. Some of these risk factors include:
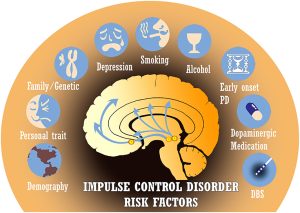
•Having a family history of impulse control disorder
•Exposure to traumatic events
•Exposure to drugs or alcohol
•Having mental health disorders, such as bipolar disorder or schizophrenia
•Taking certain medications that can contribute to impulsivity
Impulse Control Disorder vs. ADHD
A person cannot technically have an impulse control disorder unless he has some other psychological problem that causes him to misbehave or harm himself. If someone feels crazy urges without there being any apparent reason why he would be feeling them, then he more likely has attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), or another psychological problem.
Impulse Control Disorder (ICD) is a psychiatric condition that can cause people to act on impulses that are harmful to themselves or others. This disorder can present itself in people who are addicted to drugs or alcohol, or who suffer from some other psychological disorder. Impulsive behavior can be extremely harmful, both to the individual with the disorder and to their loved ones.
“Surprising numbers of Americans live with impulse-control disorders.”
Treatment Options for Impulsivity
Treatment options for impulsivity can vary depending on the individual and the symptoms that they are exhibiting. In some cases, medications such as antidepressants and antipsychotics may be prescribed in an effort to reduce impulsive behavior. These drugs can help treat underlying psychiatric conditions, allowing people to better control their impulses.
In addition to medication, therapy is another common treatment option for impulse control disorder symptoms. Behavioral therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) have proven effective for many types of mental health disorders, including ICD symptoms. Exposure therapy, a type of CBT, can be especially effective for people with impulse control disorder. This type of therapy involves exposing the individual to triggers for their impulsive behavior in a safe environment. This allows them to learn how to manage these impulses in healthy ways.
Importance of Controlling Impulses

Controlling impulses is an important part of maintaining a healthy lifestyle and relationships. Many mental health disorders are characterized by impulsivity, which can lead to harmful behaviors like addiction and self-harm. Thus, learning how to control impulses can help prevent many other mental health problems down the road. Additionally, being able to control impulses can improve interpersonal relationships with other people in your life. When you are able to resist urges that are harmful or inappropriate, it shows others that you respect and care for them.
People who suffer from impulse control disorder can experience great difficulty controlling their impulses, which can result in serious consequences. People with the disorder are at higher risk for interpersonal problems, legal issues, and mental health concerns. It is therefore extremely important for people with ICD to seek help by speaking with a mental health professional or joining support groups.
Difference Between Impulses and Choices
Impulse control disorder symptoms can make it seem like people with psychological disorders are unable to make choices or do not have control over their actions. However, impulses and choices are two different things. A choice is a conscious decision made by an individual to engage in a behavior, such as smoking or spending money. An impulse, on the other hand, is something that happens reflexively without thought or intention. For example, someone might smoke because they were having a craving and felt an overwhelming urge to light up a cigarette. Additionally, someone might spend impulsively because they want to feel good right now without thinking about tomorrow. Thus impulsivity can lead to poor choices that are harmful to the person or others.
Impulse Control Disorder Treatment

Successful treatment for impulse control disorder depends on the individual and their personal situation. Treatment options include:
•Behavioral therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT)
•Psychotherapy – This type of therapy can help people better understand impulses and develop coping strategies to help them control them. Some examples include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and dialectical behavior therapy.
•Medication, such as antidepressants or antipsychotic medications
•Religious support, including 12-step programs like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) Behavioral Impulse Control Disorder Examples
Impulsive behavior can take many different forms depending on the person suffering from the disorder. Some common examples of impulsive behaviors include: –
Spending money excessively or compulsively buying items
- Aggression toward others
- Sexual promiscuity or infidelity
- Unsafe sexual practices
- Excessive gambling or addiction to video games
Disruptive control disorder
Disruptive control disorder is a psychological condition that is characterized by a person’s inability to control their disruptive behaviors. People with this disorder often experience problems in their personal relationships and at work or school. Additionally, they may have difficulty complying with rules and regulations.
There are many different types of disruptive behaviors that can be exhibited by someone with this disorder. Some common examples include verbal outbursts, physical aggression, property destruction, and theft. People with disruptive control disorder often feel overwhelmed and out of control when they engage in these behaviors.
Conclusion
Impulse control disorder is a condition that affects the ability to resist an urge or impulse. Impulsivity can be manifested in different forms, including hyperactivity, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and obsessive-compulsive disorder. The inability to resist impulses often leads to self-destructive behavior such as drug abuse or gambling addiction. Some people are more susceptible than others due to various factors like their upbringing or genetics. For those who struggle with this mental health issue, there are treatment options available which include psychotherapy and medication management. If you think you might have symptoms of impulsivity but don’t know where to turn for help, consult your doctor today!
A Word From Therapy Mantra
Your mental health — Your psychological, emotional, and social well-being — has an impact on every aspect of your life. Positive mental health essentially allows you to effectively deal with life’s everyday challenges.
At TherapyMantra, we have a team of therapists who provide affordable online therapy to assist you with issues such as depression, anxiety, stress, workplace Issues, addiction, relationship, OCD, LGBTQ, and PTSD. You can book a free therapy or download our free Android or iOS app.


