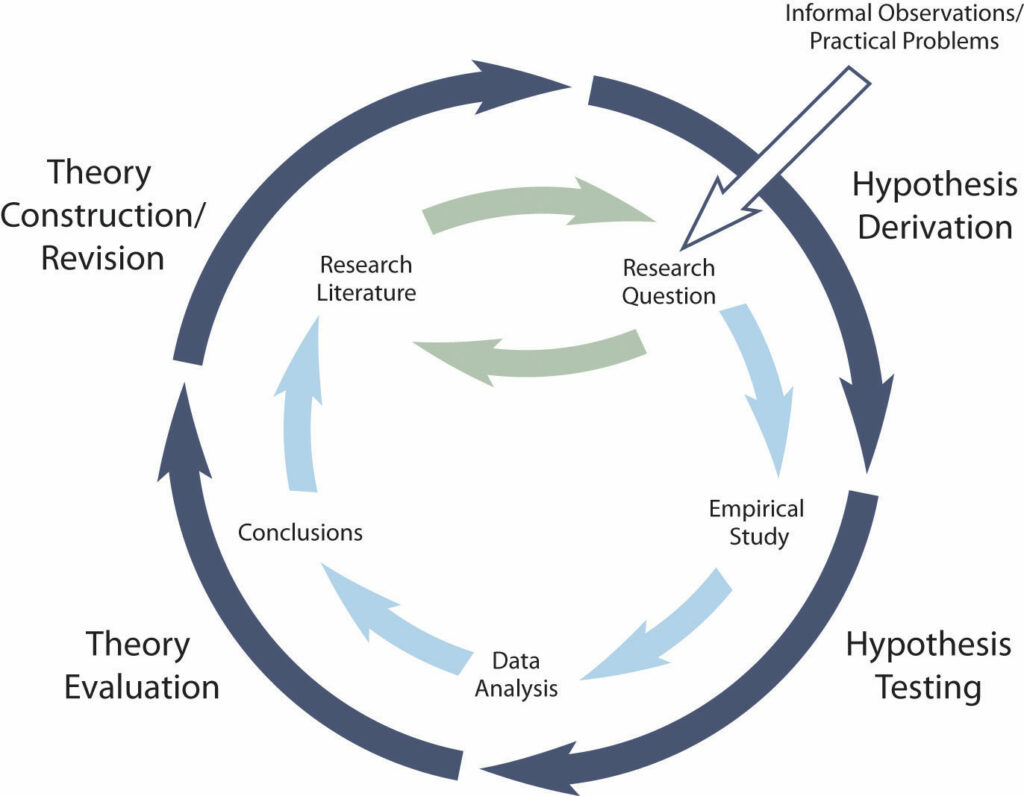
What is a theory in psychology? How important are they? What goes into making a good one. And how can you tell if a theory is sound, or needs further refinement? In this comprehensive blog post, we’ll answer all of these questions and more.
Contents
Understanding Theory In Psychology
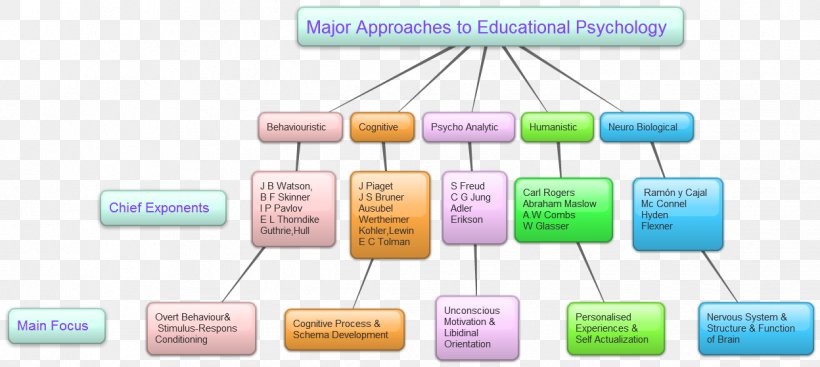 A theory in psychology is an idea that has been proven through rigorous testing and research. Theories are the backbone of our scientific understanding of human behavior.
A theory in psychology is an idea that has been proven through rigorous testing and research. Theories are the backbone of our scientific understanding of human behavior.
They provide explanations for why we act the way we do. By understanding why people act the way they do, we can make better decisions in our own lives. Consequently, we improve our relationships with others.
Role of Theory In Psychology

While theories may seem like dry, academic concepts, they actually play a vital role in our everyday lives. Theories help us make sense of the world around us. And allow us to predict (and sometimes control) human behavior.
The theory is also essential to scientific progress. Every new theory that is developed builds on what has come before it. Thus, making it possible for us to continue to learn more about the world we live in.
Propounders of Theories In Psychology
Many great psychologists have made significant contributions to our understanding of human behavior. Some of the most famous theorists in psychology include Sigmund Freud, Jean Piaget, and Albert Bandura.
Each of these psychologists developed theories that are still studied and used today. Each theory has helped us learn more about how people think, feel, and behave.
Types of Theories In Psychology
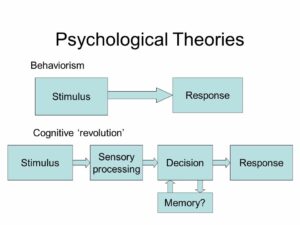
There are four major types of theory in psychology:
- Structuralist theory: This theory focuses on the structure of the mind, examining how different elements like sensations, perceptions, and thoughts are organized.
- Functionalist theory: This theory examines how mental functions (like thinking and remembering) contribute to overall psychological well-being.
- Behaviorist theory: This theory looks at how environmental stimuli influence behavior.
- Cognitive theory: This theory looks at how people think, learn, and remember information.
NOTE: Each type of theory offers a different perspective on why humans behave the way they do.
Examples of Theories In Psychology
Structuralist Theory: Sigmund Freud’s psychoanalysis
Sigmund Freud’s psychoanalysis is a classic example of structuralist theory. Freud believed that the human mind was divided into three parts:
- the id (the primitive, instinctual part of the mind),
- the ego (the realistic, rational part of the mind), and
- the superego (the moral, ethical part of the mind).
Functionalist Theory: Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is a classic example of functionalist theory. Maslow believed that human behavior is motivated by a hierarchy of needs. Starting with the most basic (physiological) and moving up to more complex (self-actualization) needs.
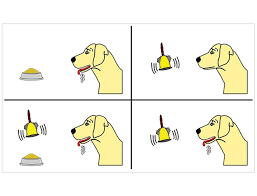
Behaviorist Theory: B. F. Skinner’s operant conditioning
B. F. Skinner’s operant conditioning is a classic example of behaviorist theory. Skinner believed that environmental stimuli (like rewards and punishments) influence behavior.
Cognitive Theory: Jean Piaget’s cognitive development theory
Jean Piaget’s cognitive development theory is a classic example of cognitive theory. Piaget believed that children think differently than adults. And that they go through a series of cognitive stages as they develop.
Theories In Psychology Vs. Other Disciplines
Theories in psychology are different than theories in other disciplines, like physics or biology. In those sciences, a theory is an overarching explanation for a wide range of phenomena. In psychology, theories tend to be more specific, providing explanations for narrow sets of observations.
For example, the theory of gravity explains why objects fall to the ground. The theory of natural selection explains how species evolve over time. Neither of these theories is specific to one area of physics or biology – they apply broadly across those fields.
In contrast, the social cognitive theory of aggression only applies to aggression. The tripartite model of depression only applies to depression. And so on.
Evaluating Relevance of Theories In Psychology
Theories don’t just develop on their own – they are draw power from the people who use them. When psychologists adopt a theory, they give it credibility. And when researchers test a theory, they lend it legitimacy. Theories in psychology are not law. But they carry a great deal of weight because they have been proven through research.
Epistemological Development
Theories must go through a rigorous process of development and testing before they receive wide acceptance. This process is known as epistemological development. For a theory to be successful, the first step is to develop it. Then, the next step is to test it against data.
If the data supports the theory, it has then predictive power. If the data does not support the theory, it is deemed to be falsifiable. A good theory will always be able to withstand rigorous testing and analysis.
NOTE: The more studies that have been conducted, the better our understanding of the theory will be.
Criteria of Truth Value
We can evaluate theories on two criteria:
- their ability to explain behavior, and
- their ability to be verified through research.
Theories that can explain a wide range of behavior and also has backing by a great deal of research are more likely to be true. In contrast to theories, that only explain a small amount of behavior or do not have much research to support their claim.
How To Tell If A Theory Is Good
There are a few things you can look for to determine if a theory is good.
- First, check to see if the theory has been peer-reviewed. This means that it has been vetted by other experts in the field and found to be sound.
- Second, look for evidence of predictive power. A good theory will be able to explain past behavior and predict future behavior.
- Finally, check for falsifiability. A good theory will be able to withstand rigorous testing and analysis.
Are All Theories In Psychology Good
No, not all theories in psychology are good. In fact, many of them are bad. But the good theories are worth the effort because they can help us understand ourselves and the world around us.
NOTE: It is important to remember that all theories have their limitations. They can only explain a certain amount of behavior. And they are always subject to change with new research.
Hearing From Experts

When it comes to psychological theories, it is important to hear from experts in the field. These experts can provide accurate information about the theories and their implications.
- One way to find experts is to look for sources by people who have a Ph.D. in psychology. These sources will be more likely to provide accurate information than sources by people who do not have a Ph.D. in psychology.
- Another way to find experts is to look for sources by members of the American Psychological Association (APA). The APA is a professional organization working to advance psychology as a science and profession.
Case Study
Evaluating Theories In Action
Let’s take a closer look at how we evaluate theories by looking at a case study.
- Theory A is a cognitive theory that suggests that people learn best through hands-on experience.
- Theory B is a behaviorist theory that suggests that people learn best through rewards and punishments.
The Key Message
To evaluate these theories, we can look at how well they predict behavior and how much research supports them. We can also look at how the theories might be helpful in practice.
Conclusion
Theories don’t just appear out of thin air – they go through a process of development and refinement. The first step is usually an idea, or hunch, that is then undergo testing through research. If the results of the research support the idea, it becomes a working theory. But this is only the beginning – theories must then need constant evaluation and an updation as new information comes to light. In a nutshell, theories are constantly evolving with new research. Thus, as our understanding of human behavior changes, so do our theories.
A Word From Therapy Mantra
Your mental health — Your psychological, emotional, and social well-being — has an impact on every aspect of your life. Positive mental health essentially allows you to effectively deal with life’s everyday challenges.
At TherapyMantra, we have a team of therapists who provide affordable online therapy to assist you with issues such as depression, anxiety, stress, workplace Issues, addiction, relationship, OCD, LGBTQ, and PTSD. You can book a free therapy or download our free Android or iOS app.