Irrational thoughts are a part of human nature. We all have them from time to time. However, for some people, such thoughts can become a serious problem that impacts their life and health. In this blog post, we will explore what irrational thoughts are, the different types of such thoughts, their causes, the associated risks, and how to cope with them. We will also hear from experts about their experiences with dealing with them. So read on and see if you tend to ruminate on them in day-to-day life.
Contents
Understanding Irrational Thoughts
Irrational thoughts are thoughts that don’t make sense and aren’t based on reality. They can be extremely intrusive and cause a lot of distress. Examples of irrational thoughts include:
- Thinking that you are a terrible person and deserve to be punished
- Thinking you are going to die or get seriously injured every time you leave the house
- Believing that someone is out to get you or that everyone is talking about you behind your back
- Constantly worrying that something bad will happen, even though there is no evidence that it will
Do We All Have Them
Most people have such thoughts from time to time. It’s a normal part of human nature. However, for some people, these thoughts can become so frequent and intense that they start to interfere with everyday life. When this happens, it’s known as an irrational thought disorder.
Irrational Thoughts Vs. Delusions
Irrational thoughts are not the same as delusions. Delusions are false beliefs that are held strongly, even in the face of contradictory evidence. For example, a person who believes that they are being followed by aliens is experiencing a delusion.
Irrational Thoughts Vs. Obsessions
Irrational thoughts are not the same as obsessions. Obsessions are repetitive and intrusive thoughts that a person cannot control. For example, a person with OCD may be obsessed with the thought of harm coming to them or their loved ones.
Irrational Thoughts Vs. Cognitive Distortions
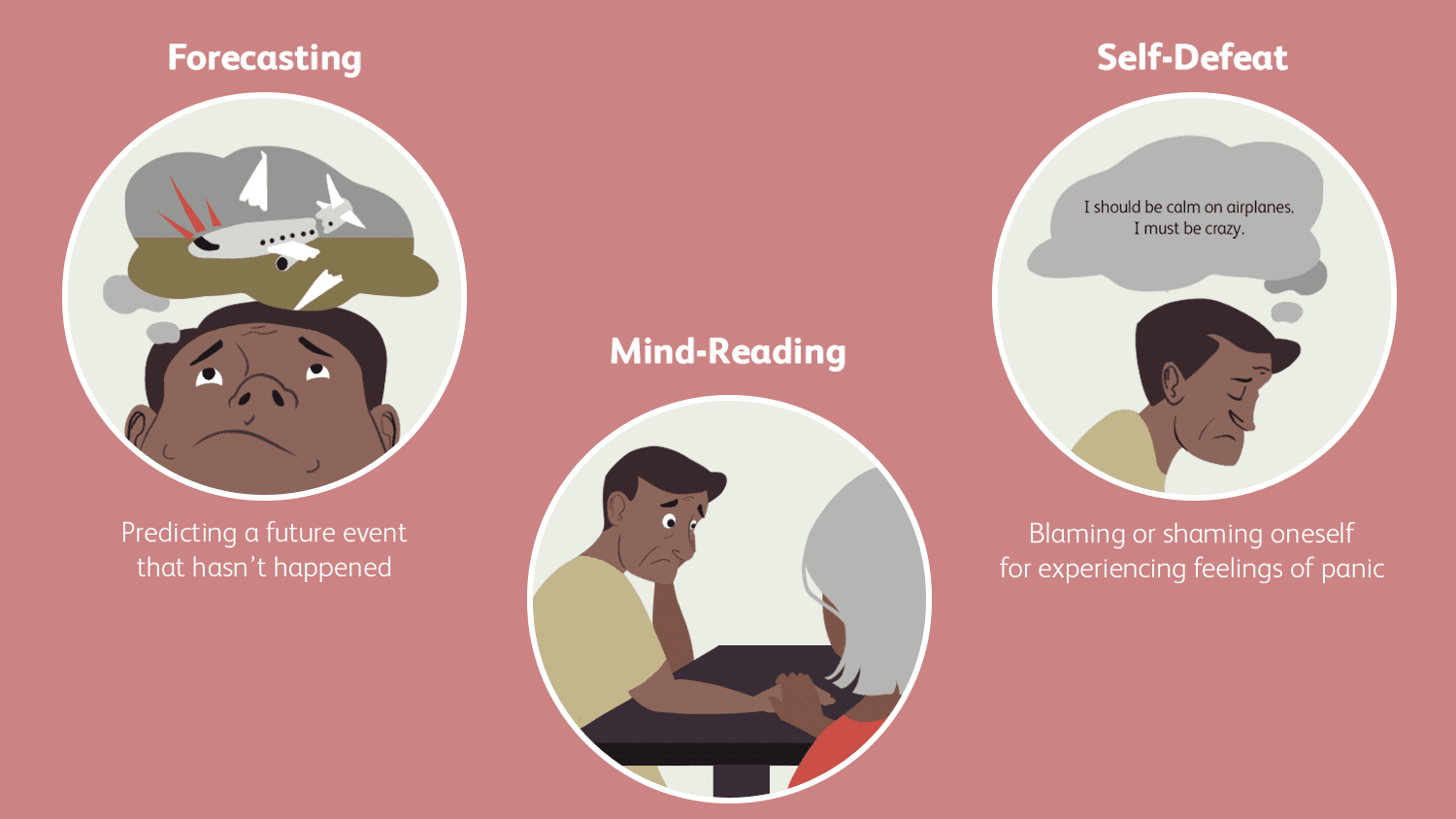
Irrational thoughts are usually characterized by their intensity and their ability to distort reality. However, cognitive distortions are specific types of irrational thoughts that can cause a lot of distress. Some common cognitive distortions include:
- Mind reading: Assuming that you know what someone else is thinking
- All-or-nothing thinking: Thinking in terms of black-and-white, good-or-bad, perfect-or-failure
- Overgeneralization: Making a general statement based on a single event
- Catastrophizing: Expecting the worst possible outcome from a situation
- Labeling and mislabeling: Calling yourself or others names, or attaching negative labels to events or situations
- Blaming: Shifting responsibility for your own actions or feelings onto others
Types of Irrational Thoughts
There are many different types of such thoughts. Some of the most common types include:
- Obsessive-compulsive thoughts: Thoughts that keep coming back over and over, no matter how hard you try to get rid of them
- Rumination: Dwelling on negative thoughts or experiences, often to the point where they are all you can think about
- Compulsive doubts: Doubting your own thoughts, feelings, and actions to the point where you can’t seem to stop
- Phobias: Fear of something that is usually irrational or unrealistic, such as spiders, heights, or public speaking
- Paranoia: Belief that others are out to get you or are talking about you behind your back
- Impulsiveness: Acting on impulse without thinking about the consequences
Causes of Irrational Thoughts
There is no single cause of such thoughts. Instead, several different factors can contribute to their development. Some of the most common causes include:
Stress: Prolonged stress can cause the brain to become overactive, which can lead to the development of irrational thoughts.
Brain activity: Abnormalities in brain function and structure have been linked to the development of irrational thoughts.
Poor coping skills: Not knowing how to deal with difficult emotions can make you more likely to develop irrational thoughts.
Trauma: Traumatic experiences can leave a person feeling unsafe and vulnerable, leading to the development of irrational thoughts as a way of coping.
Personality traits: Some personality traits, such as perfectionism and neuroticism, can make a person more prone to developing irrational thoughts.
Risk Factors of Irrational Thoughts
Several different factors can increase a person’s risk of developing such thoughts. Some of the most common risk factors include:
Genetic factors: There is some evidence that irrational thoughts may be hereditary.
Environmental factors: Exposure to traumatic events or prolonged periods of stress can increase the risk of developing irrational thoughts.
Psychological factors: Some personality traits, such as perfectionism and neuroticism, can make a person more prone to developing irrational thoughts.
Biological factors: Certain physical or medical conditions, such as anxiety or depression, can increase the risk of developing irrational thoughts.
Prone Personality Types
Several different personality types are more prone to developing suchthoughts. Some of the most common types include:
Neurotic people: People who are easily stressed and tend to worry a lot are more likely to develop irrational thoughts.
Perfectionists: People who strive for perfection often experience a lot of stress and anxiety, which can lead to the development of irrational thoughts.
People with low self-esteem: People who feel like they are not good enough or do not deserve happiness are more likely to develop irrational thoughts.
History And Development
A Condition Was Described; Monomania
The first recorded instance of irrational thoughts was in the early 1800s when a French physician named Jean-Etienne Dominique Esquirol described a condition he called “monomania.” This condition was characterized by obsessive and repetitive thoughts.
Reason Was Identified; Psychological Trauma
In the early 1900s, another French physician named Pierre Janet developed a theory that irrational thoughts were caused by psychological trauma. This theory was later expanded on by Sigmund Freud, who believed that irrational thoughts were a way of coping with difficult emotions.
A Therapy Was Developed; Cognitive therapy
In the 1950s, cognitive therapy was developed as a treatment for irrational thoughts. This therapy focuses on changing the way a person thinks about their problems and teaches them how to cope with difficult emotions in a healthy way. Today, cognitive therapy is considered the gold standard treatment for irrational thoughts.
Identifying Irrational Thoughts

The best way to identify irrational thoughts is by keeping track of your thoughts and feelings over a period of time. This can be done with a journal or a diary.
Symptoms of Irrational Thoughts
Several different symptoms can be associated with such thoughts. Some of the most common symptoms include:
Anxiety: People who have irrational thoughts often experience anxiety and fear. This can be due to the worry that their thoughts will come true or the fear of not being able to control their thoughts.
OCD: People with OCD often have repetitive and intrusive thoughts that they cannot control. These thoughts can be about anything, including harm to themselves or others.
Depression: People who have irrational thoughts often experience depression and low mood. This is because the worry and anxiety caused by their thoughts can be very overwhelming.
Decoding The Link
There are several different theories about the link between anxiety and irrational thoughts. Some of the most common theories include:
Cognitive theory: This theory suggests that people with anxiety have negative thought patterns that lead to the development of irrational thoughts.
Behavioral theory: This theory suggests that people with anxiety develop irrational thoughts as a way of coping with their fear and anxiety.
Psychodynamic theory: This theory suggests that people with anxiety have unresolved conflicts or emotional problems that lead to the development of irrational thoughts.
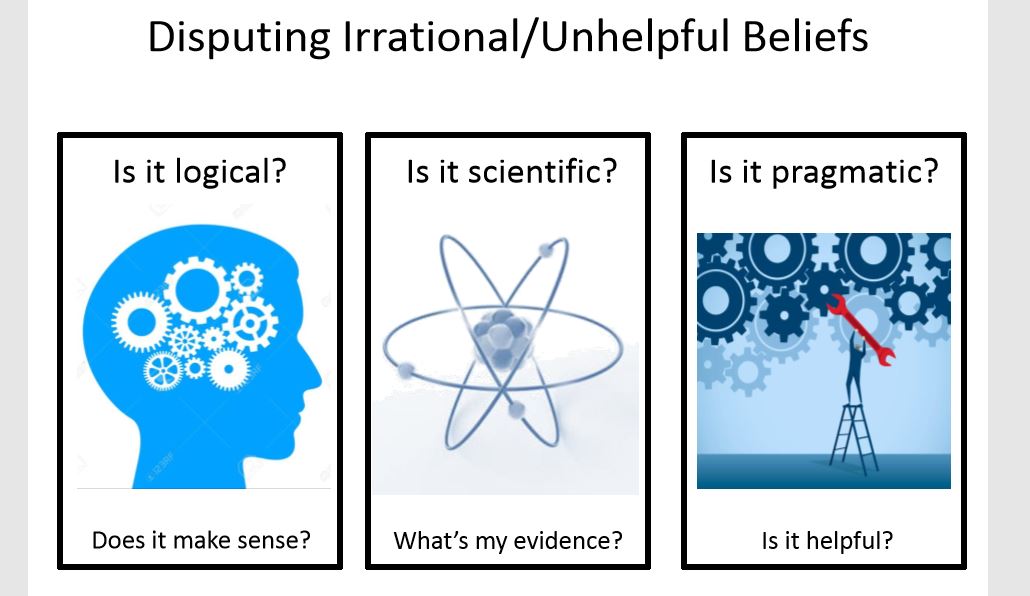
Evaluating Irrational Thoughts
Once you have identified your irrational thoughts, the next step is to evaluate them. This can be done by asking yourself a few questions, such as:
- Are my thoughts realistic?
- Do my thoughts cause me any distress?
- Is there a logical solution to the problem I’m worried about?
- Can I control my thoughts?
If you answer ‘no’ to all of these questions, then it is likely that your thoughts are irrational.
Impact on Life
These thoughts can have a significant impact on a person’s life. They can cause a lot of distress and anxiety, which can lead to problems such as:
Personal Life: Irrational thoughts often cause people to withdraw from their loved ones. This can lead to relationship problems and social isolation.
Professional Life: People who have irrational thoughts often find it difficult to concentrate on their work. This can lead to poor work performance and job satisfaction.
Social Life: People who have irrational thoughts often find it difficult to participate in social activities. This can lead to feelings of loneliness and isolation.
Impact on Health
These thoughts can also harm a person’s health. This can lead to mental symptoms as well as physical health problems.
Mental health: People who have irrational thoughts are at an increased risk of developing mental health problems, such as anxiety and depression.
Physical Health: Irrational thoughts can also lead to physical health problems, such as headaches, chest pain, and gastrointestinal problems.
Disrupting Irrational Thoughts
There are several different ways that people can cope with irrational thoughts. Some of the most common methods include:
Self-help Tips
Several self-help tips can be useful for people who have such thoughts. These include:
Identifying your triggers: Try to identify what triggers your irrational thoughts. This can help you to avoid these triggers in the future.
Challenging your thoughts: Once you have identified your irrational thoughts, try to challenge them. This can be done by asking yourself whether there is any evidence to support your thoughts.
Replacing negative thoughts with positive thoughts: Replace any negative thoughts with positive ones. This can help to reduce your anxiety and improve your mood.
Self-help Tools
Several self-help tools can be useful for people who have such thoughts. These include:
Problem-solving: Problem-solving can be a useful tool for dealing with the anxiety and fear caused by irrational thoughts.
Visualization: Visualization can be a helpful technique for coping with intrusive thoughts. It involves picturing yourself in a calm and peaceful place.
Positive thinking: Positive thinking can be a helpful way of dealing with irrational thoughts. It involves replacing negative thoughts with positive ones.
Thought stopping: Thought stopping is a technique that can be helpful to stop intrusive thoughts. This involves saying ‘stop’ or ‘no’ to yourself when you have an irrational thought.
Relaxation techniques: Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and muscle relaxation, can help to reduce the stress and anxiety associated with irrational thoughts.
Mindfulness meditation: Mindfulness meditation can be a helpful way of dealing with intrusive thoughts. It involves focusing on the present moment and accepting your thoughts and feelings, without judgment.
Support groups: Support groups can provide people with a safe place to share their experiences and learn from others who are going through similar challenges.
Lifestyle Tips
Several lifestyle changes can be helpful for people who have such thoughts. These include:
Exercise: Exercise can help to reduce stress and anxiety. It can also help to improve your mood and sleep quality.
Healthy eating: Eating a healthy diet can help to improve your mental health. It can also help to reduce the symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Getting enough sleep: Getting enough sleep is important for your mental health. It can also help to reduce the symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Reducing stress: Stress can trigger irrational thoughts. Try to reduce stress by doing things that you enjoy, such as exercise, relaxation techniques, or meditation.
Diet Tips
Several different diet tips can be useful for people who have such thoughts. These include:
Eating regular meals: Eating regular meals can help to regulate your blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of mood swings.
Avoiding caffeine and alcohol: Caffeine and alcohol can increase anxiety levels. It is best to avoid these substances if you are struggling with irrational thoughts.
Eating plenty of fruits and vegetables: Eating plenty of fruits and vegetables can help to boost your mood and improve your mental health.
Getting enough omega-three fatty acids: Omega-three fatty acids are important for brain health. They can be found in oily fish, such as salmon, trout, and mackerel.
NOTE: According to nutritional psychology; “we become what we eat!”
Sleep Tips
Several different sleep tips can be useful for people who have such thoughts. These include:
Establishing a regular sleep routine: Having a regular sleep routine can help to improve your sleep quality.
Creating a relaxing bedtime routine: Creating a relaxing bedtime routine, such as reading or taking a bath, can help you to wind down before bed.
Make sure your bedroom is dark and quiet: A dark and quiet bedroom is conducive to sleep. Try to reduce noise and light exposure in your bedroom.
Talking to Professional

If you find that your irrational thoughts are causing you a lot of distress, then it may be useful to talk to a professional. They can provide support and guidance and teach you coping strategies for dealing with such thoughts. Several different professionals can help, including:
Psychologists: Psychologists can provide Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), which is an effective treatment for anxiety.
Psychiatrists: Psychiatrists can prescribe medication, such as antidepressants, which can be helpful for people who have anxiety.
Counselors: Counselors can provide support and guidance. They can also teach you coping strategies for dealing with such thoughts.
If you find that your irrational thoughts are harming your life, then it is important to seek help. This can include:
- Having difficulty concentrating at work
- Feeling overwhelmed by anxiety
- Experiencing physical health problems
- Finding it difficult to socialize with others
- Suicidal thoughts or attempts
Therapies
Several different therapies can be helpful for people who have such thoughts. Some of the most common therapies include:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a type of therapy that focuses on changing the way you think about your thoughts and feelings. It is an effective treatment for anxiety.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): DBT is a type of therapy that focuses on improving your emotional regulation skills. It can be helpful for people who have difficulty managing their emotions.
Exposure Therapy: Exposure therapy is a type of therapy that involves exposure to the things that trigger your anxiety. This can help you to learn to manage your anxiety.
Medication
Several different medications can be helpful for people who have such thoughts. Some of the most common medications include:
Antidepressants: Antidepressants are a type of medication that can be helpful for people who have anxiety. They work by changing the levels of chemicals in the brain.
Anti-anxiety medications: Anti-anxiety medications are a type of medication that can be helpful for people who have anxiety. They work by reducing the symptoms of anxiety.
Beta-blockers: Beta-blockers are a type of medication that can be helpful for people who have anxiety. They work by blocking the effects of adrenaline.
NOTE: Always speak to a doctor before starting any new medication. Because there are several different medications that can be helpful for people who have anxiety, it is important to speak to a doctor to find the best medication for you.
Case Study
I am a 26-year-old woman who has been struggling with anxiety for the past few years. I have tried several different treatments, but nothing has really helped. Recently, my doctor prescribed me medication for my anxiety.
I was hesitant to take it, but I decided to give it a try. After starting the medication, I noticed a difference within a few weeks. My anxiety was much more manageable, and I was able to cope with my irrelevant thoughts.
Hearing From Experts
There is a lot of research on such thoughts, and researchers are still learning more about them. Some of the latest findings come from experts in the field, such as:
Dr. Aaron T. Beck: Dr. Beck is a researcher who has studied irrational thoughts for many years. He is the creator of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), which is an effective treatment for anxiety.
Dr. David A. Clark: Dr. Clark is a researcher who has studied irrational thoughts and their relationship to anxiety. He has developed several different therapies, including exposure therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy.
Brain Activity
There is also a lot of research being done on the brain activity of people who have irrational thoughts. It has been found that there are differences in the way that the brains of people with anxiety process information. This research is still in its early stages, but we can hope that it will lead to better treatments for anxiety in the future.
Resources
If you are struggling with such thoughts, several resources can help. Some of the most popular include:
American Psychological Association (APA): The APA is a nonprofit organization that provides information and resources about psychology.
National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI): NAMI is a nonprofit organization that provides information and resources about mental illness.
Conclusion
Irrational thoughts are a common symptom of anxiety. They can be very distressing, but there are treatments available that can help. If you are struggling with such thoughts, please talk to your doctor or a counselor. They can help you find the treatment that is right for you. There is also a lot of helpful information available online, including on this website.
A Word From Therapy Mantra
Your mental health — Your psychological, emotional, and social well-being — has an impact on every aspect of your life. Positive mental health essentially allows you to effectively deal with life’s everyday challenges.
At TherapyMantra, we have a team of therapists who provide affordable online therapy to assist you with issues such as depression, anxiety, stress, workplace Issues, addiction, relationship, OCD, LGBTQ, and PTSD. You can book a free therapy or download our free Android or iOS app.


