Anti-anxiety medications (anti-anxiety meds) are a type of medication helpful to treat anxiety disorders. In this article, we will discuss anti-anxiety medications, their action mechanism, side effects, and risks for taking them.
Contents
- 1 Understanding Anxiety
- 2 Knowing About Anti-anxiety Medications
- 3 Administering Anti-anxiety Medications
- 3.1 How Anti Anxiety Medications Are Available
- 3.2 How Should I Take Anti Anxiety Medications
- 3.3 What Happens If I Miss Dose Of Anti Anxiety Medications
- 3.4 What Happens If I Overdose On Anti Anxiety Medications
- 3.5 How Long Does It Take For Anti Anxiety Medications To Work
- 3.6 How To Safely Stop Taking Anti Anxiety Medications
- 4 Evaluating Anti-anxiety Medications
- 5 Summary of FDA Black Box Warnings
- 6 Experts’ Opinion About Anti-anxiety Medications
- 7 Conclusion
- 8 A Word From Therapy Mantra
Understanding Anxiety
Anxiety is a feeling of worry, nervousness, or fear. It can be mild or severe and may come and go quickly or last for a long time. People with anxiety disorders have excessive anxiety that interferes with their daily life.
Types of Anxiety Disorders
Phobias: Phobias are fears of certain objects or situations that are excessive and irrational. People with phobias often avoid the things they are afraid of, which can significantly interfere with their daily life.
Selective mutism: Selective mutism is a condition in which children do not speak in certain social situations, such as at school or with unfamiliar people, even though they can speak normally in other settings.
Anxiety Disorders
There are many different types of anxiety disorders, including:
Panic disorder: Panic disorder is a condition in which people experience sudden feelings of terror or fear called panic attacks. These panic attacks can occur at any time and without warning.
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD): GAD is a condition characterized by excessive, uncontrollable worry about everyday things. People with GAD often have trouble sleeping and concentrating, and feel restless and tense.
Social anxiety disorder: Social anxiety disorder is a condition in which people have an excessive fear of social situations. People with social anxiety often feel uncomfortable and anxious in situations where they are around other people, such as parties or large groups.
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD): PTSD is a condition that develops after someone has experienced a traumatic event such as a natural disaster, car accident, sexual assault, or war. People with PTSD often have flashbacks and nightmares, feel tense, and are easily startled.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD): OCD is a condition in which people have recurring thoughts, urges, or images that cause them distress. To cope with these symptoms, people with OCD perform rituals called compulsions to reduce their distress.
Separation anxiety disorder: Separation anxiety disorder is a condition in which people experience extreme fear or worry about being separated from certain people, such as family members or close friends. People with separation anxiety may have trouble leaving home for work or school and prefer to stay at home rather than be away from loved ones for long periods.
Knowing About Anti-anxiety Medications
Anti-anxiety medications are a type of medication used to treat anxiety disorders. Anti-anxiety medications are also referred to as anxiolytics. Antianxiety medications work by reducing a person’s feelings of anxiety and fear.
They may be prescribed for the short term, such as one or two weeks, to treat immediate episodes of anxiety that can occur due to a specific event or situation. They may also be prescribed on a long-term basis to help manage chronic anxiety disorders.
Types of Anti-anxiety Medications

There are many different types of anti-anxiety medications, including:
Benzodiazepines
They are a type of medication that is used to treat anxiety, panic attacks, and insomnia. These medications are effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety and helping people to sleep better. They work by slowing down the activity of the brain and making a person feel more relaxed.
Benzodiazepines include drugs such as:
Buspirone
Buspirone is a type of medication that may be used to treat anxiety. It works by increasing the activity of serotonin, a neurotransmitter in the brain that helps regulate moods.
Examples of buspirone include:
- BuSpar and
- Buspar Dividose
Beta-blockers
They are a type of medication that is used to treat heart conditions such as high blood pressure and atrial fibrillation, but they may also be prescribed for people with social anxiety disorder.
Beta-blockers work by reducing the activity of adrenaline and other chemicals in the body that can cause the heart to beat too fast or irregularly. This can help to control symptoms of anxiety, such as a racing heart or sweating.
Examples of beta-blockers include:
- Atenolol (Tenormin),
- Bisoprolol (Zebeta),
- Metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol XL), and
- Propranolol (Inderal)
Antidepressants
They are a type of medication that is used to treat depression, but they may also be prescribed for people with anxiety disorders.
Antidepressants work by increasing the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. People who have both an anxiety disorder and depression often respond well to antidepressants.
Examples of antidepressants include:
- Citalopram (Celexa),
- Escitalopram (Lexapro),
- Fluoxetine (Prozac),
- Paroxetine (Paxil), and
- Sertraline (Zoloft)
Action Mechanism of Anti-anxiety Medications
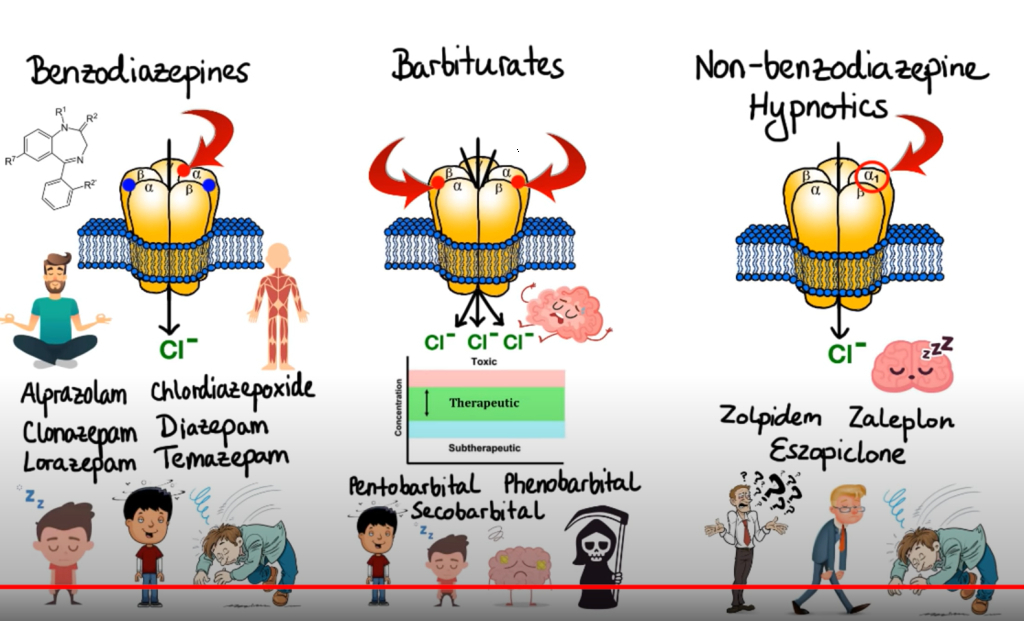
How anti-anxiety medications work depends on the type of medication. Benzodiazepines, buspirone, and beta-blockers all act as central nervous system (CNS) depressants.
The CNS controls involuntary actions in the body such as respiration and digestion, but it also controls moods and emotions. When a person takes anti-anxiety medication, the drug alters how neurotransmitters are sent and received by nerve cells.
Important Information I Should Know About Anti-anxiety Medications
- People who have a history of drug or alcohol abuse should not take benzodiazepines, as they can be habit-forming.
- Before taking anti-anxiety medication, it is important to discuss the risks and benefits with a doctor. Anti-anxiety medications can be habit-forming and may not be safe for everyone to take.
- People who have COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder), sleep apnea, liver disease, or kidney disease may need to avoid certain types of anti-anxiety medications due to the risk for side effects.
- People who have anxiety disorders may experience a worsening of symptoms, and they might also become dependent on the medication over time. For this reason, it is important to take anti-anxiety medications as prescribed by a doctor and not stop taking them without their advice.
NOTE: Anti-anxiety medications can be helpful for many people who struggle with anxiety, but they are not a cure. People should continue to use therapies and lifestyle changes along with medication so that symptoms do not return once the drugs stop working or when treatment ends.”
Pregnancy And Specific Concerns About Anti-anxiety Medications
Some anti-anxiety medications should not be taken during pregnancy, as they may increase the risk of birth defects. It is important for women who are pregnant or thinking of becoming pregnant to discuss any concerns about taking anti-anxiety medications with their doctor.
NOTE: People who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take benzodiazepines, as they can cross the placenta and enter into breast milk.
Things to Discuss With Doctor Before Taking Anti-anxiety Medications
People need to discuss their medical history with a doctor before starting anti-anxiety medication, as some drugs may be unsafe in certain situations. It is also important to tell the doctor about any other medications or supplements that are being taken at the same time, as these could interact with anti-anxiety medications.
NOTE: Antifungal or seizure medications may be less effective when taken at the same time as some anti-anxiety drugs.
Administering Anti-anxiety Medications

When taking anti-anxiety medication, it is important to follow the doctor’s instructions. The drug may be taken orally in the form of a pill or liquid, or it may be injected. Some medications are available as patches that can be placed on the skin.
How Anti Anxiety Medications Are Available
There are several different anti-anxiety medications available. Most are prescription drugs that are only available from pharmacies when a doctor has prescribed them, but some can be bought over the counter without a prescription.
How Should I Take Anti Anxiety Medications
Taking anti-anxiety medication is usually a short-term solution to manage severe anxiety. People who are taking these drugs should be regularly reviewed so that the doctor can assess whether they need to continue taking them or can stop treatment.
NOTE: Some anti-anxiety medications can cause drowsiness or dizziness, so it is important to avoid alcohol.
What Happens If I Miss Dose Of Anti Anxiety Medications
If a dose of anti-anxiety medication is missed, it should be taken as soon as possible. If it is close to the time for the next dose, the missed dose should be skipped and the regular schedule resumed.
What Happens If I Overdose On Anti Anxiety Medications
If someone overdoses on anti-anxiety medications, they should go to the nearest hospital emergency room immediately. Symptoms of an overdose can include:
- Drowsiness,
- Irritability, and
- Confusion
How Long Does It Take For Anti Anxiety Medications To Work
Some people may feel relief from symptoms of anxiety within a few days of starting anti-anxiety medication, but for most people, it takes two to four weeks.
NOTE: If anti-anxiety medications are not working for a person or cause intolerable side effects, they should speak to their doctor about switching to another medication. Sometimes the first drug does not work for some people, so it is important to keep trying.
How To Safely Stop Taking Anti Anxiety Medications
It is important for people who are taking any kind of prescription drug to see a doctor regularly so that he/she can monitor their condition and assess whether they need to continue taking the drug or stop treatment.
People who are taking anti-anxiety medications should speak to their doctor about how best to safely stop taking them. Some people may be able to stop taking the medication gradually, while others may need to stop abruptly.
Regardless of how it is done, it is important to do so under a doctor’s supervision to avoid any potential complications.
NOTE: Always speak with a doctor before stopping any kind of prescription drug.
Evaluating Anti-anxiety Medications
A doctor will usually only prescribe anti-anxiety medications after a person has been thoroughly evaluated. This may include a physical examination, blood tests, and/or urine tests.
Possible Side effects of Anti-anxiety Medications
Most people who take anti-anxiety medications do not experience any side effects, and the most commonly reported ones are usually mild. But some common and serious side-effects include:
Common Side-effects
- Drowsiness or fatigue,
- Dizziness,
- Nausea and vomiting,
- Headache, and
- Sinus congestion.
Rare Side effects
Some rare side effects of anti-anxiety medications can include:
- Hallucinations,
- Seizures,
- Suicidal thoughts and behavior,
- Confusion, and
- Insomnia
Precautionary Note
If a person experiences side effects while taking anti-anxiety medications, they should consult their doctor as soon as possible. The doctor may be able to change the dosage or switch a person to a different drug that does not have the same side effects. Furthermore, if a person experiences any of the rarer side effects, including hallucinations, suicidal thoughts or behavior, confusion, or uncontrolled muscle movements while taking anti-anxiety medications, they should seek medical attention immediately.
Risks For Taking Anti-anxiety Medication For a Long Time
Anti-anxiety medications may not act well in a long term. They can work well as a short-term solution while other treatments, such as therapy or lifestyle changes, are in the mix.
Some risks associated with taking anti-anxiety medications for an extended period include:
Side effects: People who take anti-anxiety medications for a long time may experience more severe side effects than those who take them for a short time.
Dependence and addiction: It is possible to become addicted to anti-anxiety medications, and people who are dependent on them may experience withdrawal symptoms if they stop taking them.
Interaction with other drugs: A person taking anti-anxiety medications may not be able to take other drugs, such as antifungals or seizure medication.
NOTE: It is important for people who are taking any kind of prescription drug to see a doctor regularly so that he/she can monitor their condition and assess whether they need to continue taking the drug or stop treatment.
Medications That May Interact With Anti-anxiety Medications
Some common medications that can interact with anti-anxiety medications include:
Antidepressants: Some antidepressants, such as SSRIs and SNRIs, can cause drowsiness if taken with anti-anxiety medications. This may increase the risk of falls or other accidents in older people.
Anticonvulsants: Anticonvulsants helpful to treat seizures may also interact with anti-anxiety medications. So a person taking both drugs needs close monitoring.
Benzodiazepines: Benzodiazepines are a type of anti-anxiety medication that can be addictive and may increase the risk of overdose if taken with other drugs, including anti-anxiety medications.
Herbal supplements: Some herbal supplements, such as St. John’s wort, may interact with anti-anxiety medications and increase the risk of side effects.
HIV/AIDS medications: Some HIV/AIDS medications, such as ritonavir and nelfinavir, can interact with anti-anxiety medications and cause serious side effects.
Epilepsy medications: Anti-anxiety medications may interact with certain anti-epilepsy drugs, such as phenytoin and carbamazepine, and increase the risk of seizures or other problems.
Sedatives: Sedatives are a type of drug that can slow down the central nervous system, causing drowsiness or sleepiness. You should not be taking them with anti-anxiety medications.
NOTE: A person taking any kind of prescription drug should speak to their doctor about any other drugs or supplements that they are using.
Alternatives To Anti-anxiety Medications
There are several alternatives to anti-anxiety medications in addition to, or instead of, taking medication. As some people find that using complementary and alternative therapies, such as yoga or meditation, can help to reduce their anxiety symptoms.
Therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of therapy that can help people learn how to change the thoughts and behaviors that contribute to their anxiety.
Exercise: Regular exercise can help reduce stress and anxiety by increasing the production of feel-good chemicals, such as endorphins, in the brain.
Dietary changes: Some research suggests that eating a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables may reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety disorders.
Supplements: Some people may find that taking supplements, such as omega-fatty acids or vitamins B and C, can help reduce symptoms of anxiety.
Meditation or mindfulness: Mindfulness meditation is effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety in some people.
Relaxation techniques: Deep breathing and other relaxation techniques may help some people with anxiety disorders manage their symptoms.
NOTE: If a person does not feel that their symptoms are adequately under control by medication alone, he or she may want to explore these other options. Contrarily, they can also be the first line of defense by doing away with the need for relying on medications.
Natural Anti-anxiety Medications
There are a number of natural anti-anxiety medications that may help to reduce anxiety symptoms without the side effects that can occur with prescription drugs.
Kava: Kava is an herbal supplement made from the root of a plant native to the South Pacific islands. And it is a folk remedy for anxiety and stress for centuries.
L-theanine: L-theanine is an amino acid in green tea. Research shows that it helps reduce anxiety and stress.
Valerian root: Valerian root is a herbal supplement, effective to treat insomnia and anxiety.
Passionflower: Passionflower is a herb that is often helpful to treat insomnia and anxiety.
Magnesium: Magnesium is a mineral that may help reduce symptoms of depression, as well as stress and anxiety disorders.
Ashwagandha: Ashwagandha is an herbal supplement that may help with sleep issues, such as insomnia, and other conditions, such as anxiety and stress.
NOTE: While some people find that these natural anti-anxiety medications work well for them, others may find that they are not as effective as prescription drugs. Speak to a healthcare provider if you have an interest in trying any of these supplements.
Summary of FDA Black Box Warnings
The FDA has issued black box warnings for several anti-anxiety medications, including benzodiazepines and barbiturates. A black box warning is the strongest type of warning that the FDA can issue for a drug.
Benzodiazepines: The benzodiazepine class of drugs includes Valium (diazepam), Xanax (alprazolam), and Klonopin (clonazepam). These drugs are one medicinal option for the treatment of anxiety, panic attacks, and insomnia. However, the benzodiazepine class of drugs comes with an increased risk of addiction, overdose, and death.
Barbiturates: Barbiturates are a class of drugs that were once a medicinal option to treat anxiety, but they are no longer reliable. Because they can be addictive and may cause serious side effects. The FDA has issued black box warnings for the anti-anxiety medications phenobarbital (Luminal), secobarbital (Seconal), pentobarbital (Nembutal), and thiopental sodium.
DISCLAIMER: The information in this blog post is for educational purposes. We advise you not to consider it as a substitute for the advice of a practicing physician.
Experts’ Opinion About Anti-anxiety Medications
On Benzodiazepines
“There is a lot of controversy about the use of benzodiazepines, and I think that their use comes with a lot of caution,” said Dr. Victor Reus, a professor of psychiatry at the University of California, San Francisco. “I’m don’t oppose their use in certain situations, but I think professionals should prescribe them very judiciously and only for a short period.”
On Barbiturates
“People should avoid Barbiturates as much as possible,” said Dr. Mark Siegel, a professor of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego. “There is no reason to use them anymore because there are better alternatives.”
On Alternative Therapies
“Mindfulness meditation is helpful for people with anxiety disorders,” said Dr. Elizabeth Hoge, an associate professor of psychiatry at the Georgetown University Medical Center in Washington, D.C. “It can help reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.”
On Their Anti Stance
“I have seen some patients who were suffering from severe anxiety, but they didn’t want to take medication because they thought it would make them gain weight,” said Dr. David Kupfer, a professor of psychiatry at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine. “But I think that’s a misconception. Many anti-anxiety medications don’t cause weight gain.”
Case Study
John is a 45-year-old man who has a generalized anxiety disorder. He is on a prescription and taking Xanax (alprazolam) for six months. His anxiety symptoms have improved significantly, and he has not experienced any problems with addiction or abuse.
Precautionary Tip
“Xanax is a very effective medication for anxiety, but I would not recommend it for everyone,” said Dr. David Kupfer, a professor of psychiatry at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine. “I advise people to use them only in cases where there is a high risk of relapse or overdose.”
Conclusion
Anti-anxiety medications can be a valuable tool for treating anxiety disorders, but their use comes with caution. There are many different types of anti-anxiety medications available, and each person responds differently to them. It is important to work with a doctor to find the medication that is suitable and effective for you.
A Word From Therapy Mantra
Your mental health — Your psychological, emotional, and social well-being — has an impact on every aspect of your life. Positive mental health essentially allows you to effectively deal with life’s everyday challenges.
At TherapyMantra, we have a team of therapists who provide affordable online therapy to assist you with issues such as depression, anxiety, stress, workplace Issues, addiction, relationship, OCD, LGBTQ, and PTSD. You can book a free therapy or download our free Android or iOS app.


