If you have a loved one who suffers from OCD or sensory issues, you know that it can be difficult to understand what they are going through. It’s hard to know what to do to help them and make them feel comfortable. In this blog post, we will discuss some of the basics of OCD and sensory issues so that you can better understand your loved one. We will also provide some tips on how you can help them manage their disorder.
Contents
- 1 What Is OCD?
- 2 What Are Sensory Issues?
- 3 How Are OCD And Sensory Issues Related?
- 4 What Are The Risk Elements?
- 5 What Are The Consequences?
- 5.1 Difficulty concentrating or paying attention
- 5.2
- 5.3 Trouble sleeping
- 5.4 Problems with school or work performance
- 5.5 Social isolation and withdrawal
- 5.6 Suicidal thoughts or attempts
- 5.7 Substance abuse
- 5.8 Eating disorders
- 5.9 Excessive sweating or trembling
- 5.10 Lightheadedness or dizziness
- 5.11 Stomachaches or headaches
- 5.12 Muscle tension or pain
- 6 How Can Therapies Help?
- 7 How Can Self-Care Tips Help?
- 8 Conclusion
What Is OCD? 
OCD, or Obsessive Compulsive Disorder, is a mental disorder that causes sufferers to have repetitive and intrusive thoughts (obsessions) that lead them to perform certain actions (compulsions) in an attempt to relieve anxiety.
What Are Sensory Issues? 
Sensory issues are problems with the way the nervous system processes information from the senses. This can make it hard to do everyday activities, like going to school or work. Sensory issues can be mild, like feeling a little overwhelmed in a noisy room.
What Are The Subtypes?
There are four main types of sensory issues:
- Auditory processing disorder (APD): This is when someone has trouble understanding what they hear. They may have a hard time following directions or keeping track of a conversation.
- Visual processing disorder (VPD): This is when someone has trouble understanding what they see. They may have a hard time reading or doing other activities that require vision.
- Tactile defensiveness: This is when someone does not like to be touched, or they may be sensitive to certain textures or fabrics.
- Olfactory/gustatory sensitivity: This is when someone has a strong reaction to certain smells or tastes.
How Are OCD And Sensory Issues Related? 
OCD and sensory issues share a lot of common ground. There are several ways that OCD and sensory issues can overlap.
For example, people with OCD may obsessively wash their hands because they fear contamination from germs. This can be related to a sensory issue such as a fear of textures or smells.
People with OCD may also avoid certain foods because of concerns about contamination or choking. This avoidance can be related to a sensory issue such as texture aversion or sensitivities to smell or taste.
People with both OCD and sensory issues may have a hard time tolerating certain textures, smells, tastes, or sounds. They may also have difficulty with touch, such as feeling uncomfortable when someone else touches them or being unable to tolerate certain fabrics. These sensitivities can make everyday activities like eating, getting dressed, and going to the dentist very difficult.
What Are The Risk Elements?
Many risk elements can cause OCD and sensory issues. Some very common causes include:
Genetics
OCD is believed to have a strong genetic component, with studies showing that first-degree relatives of people with OCD are up to six times more likely to develop the condition than the general population.
Sensory processing disorder also appears to have a genetic basis, with studies suggesting that it runs in families. SPD is thought to be caused by an overabundance of certain types of receptors in the brain, which results in an increased sensitivity to sensory input. This may be due to a genetic mutation or abnormalities in brain development.
Trauma
When faced with a traumatic event, some individuals may develop maladaptive coping mechanisms in an attempt to deal with the psychological distress they are experiencing. These maladaptive coping mechanisms can include things like avoidance behaviors, numbing, dissociation, and others.
While these behaviors may provide temporary relief from the distress, they ultimately serve to perpetuate it by preventing the individual from processing and resolving the trauma.
Another way that trauma can cause OCD and sensory issues is through changes in brain structure and function. Individuals who have experienced trauma often have changes in their brain structure and function that are similar to those seen in individuals with OCD and other mental disorders. These changes in the brain can lead to the development of symptoms of OCD and sensory issues.
Stress
There are several possible explanations for why stress may contribute to OCD and sensory issues. One theory is that stress alters the balance of certain chemicals in the brain, which can lead to changes in thinking and behavior.
Additionally, stressful experiences may trigger memories of past trauma or difficult experiences, which can contribute to intrusive thoughts and compulsions. Finally, chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to developing mental health conditions.
Anxiety
Anxiety can lead to hypervigilance, which is when a person is constantly on the lookout for threats. This can make people with anxiety more likely to notice small changes in their environment or their bodies, which can trigger OCD symptoms. For example, someone with anxiety might become obsessed with making sure that all the doors in their house are locked because they are afraid of being burglarized.
Second, anxiety can also cause people to have difficulty processing information from their senses. This means that they may be more sensitive to certain sounds, smells, or textures than other people. This can make everyday activities like going to the grocery store or riding on public transportation very difficult for people with anxiety.
Depression
People with depression may become fixated on certain ideas or behaviors, which can lead to OCD-like symptoms. Additionally, Depression may also cause changes in brain chemistry that can lead to Sensory Processing Disorder (SPD).
These changes can make it difficult for someone to process information from their environment, resulting in unusual or intense reactions to everyday stimuli. Finally, depression can also lead to fatigue and sleep problems, which can further exacerbate both OCD and SPD symptoms.
Substance Abuse
There are a few different ways that substance abuse can cause OCD and sensory issues. One way is by causing changes in the brain. These changes can alter the way that messages are sent between different parts of the brain, which can lead to OCD and sensory issues.
Another way that substance abuse can cause these disorders is by increasing the levels of certain chemicals in the brain, such as serotonin and dopamine. This can also lead to changes in how messages are sent between different parts of the brain, which can again result in OCD and sensory issues.
Low Self-Esteem
Individuals with low self-esteem may be more likely to engage in repetitive and/or compulsive behaviors as a way of seeking approval or validation from others. Additionally, low self-esteem can lead to heightened anxiety and fearfulness, both of which can trigger obsessive thoughts and/or sensory overload.
Individuals who suffer from low self-esteem may also be more likely to have negative core beliefs about themselves (e.g., “I’m not good enough,” “I’m worthless,” etc.), which can further contribute to the development of OCD and/or sensory issues.
Perfectionism
When we’re perfectionists, we tend to set incredibly high standards for ourselves. We expect ourselves to be able to do things perfectly, and often get upset or anxious when we don’t meet those standards. This can lead to OCD-like behaviors, such as spending excessive amounts of time on something to make sure it’s perfect or becoming extremely upset over small mistakes.
Sensory issues can also be exacerbated by perfectionism. For people with Sensory Processing Disorder (SPD), certain sounds, textures, or lights can be overwhelming and cause a great deal of distress. This can lead to an increase in our symptoms and make it difficult to cope with everyday life.
Lack Of Coping Skills
A lack of coping skills can cause OCD and sensory issues in several ways. For example, someone with OCD might have difficulty processing and healthily responding to information. This can lead to them fixating on certain thoughts or ideas, which can then trigger obsessive and intrusive behaviors.
Alternatively, someone with sensory issues might have difficulty regulating their emotions, which can lead to anxiety and stress. This can then lead to them avoiding certain situations or objects, which can further exacerbate their symptoms.
Poor Emotional Regulation
There are many different ways that poor emotional regulation can cause OCD and sensory issues. One way is by causing a person to become overly sensitive to their environment. This can lead to them feeling like they need to constantly clean or organize their surroundings to feel safe.
Another way poor emotional regulation can cause OCD and sensory issues are by causing a person to have intrusive thoughts or images that are hard to control. These thoughts can be so disturbing that they cause the person a great deal of anxiety and fear.
Finally, poor emotional regulation can also cause a person to have trouble processing information correctly. This can lead to them making mistakes when trying to perform tasks or remember things.
What Are The Consequences?
OCD and sensory issues can have several consequences, including:
Difficulty concentrating or paying attention
There are a few key ways that OCD and sensory issues can result in difficulty concentrating or paying attention. One is when the individual is experiencing intrusive thoughts, images, or impulses that are so distressing that they interfere with the ability to focus on anything else.
Another way that OCD and sensory issues can interfere with concentration is when an individual is engaging in compulsive behaviors like checking or repeating. This can take up so much time and mental energy that it’s difficult to focus on anything else.
Trouble sleeping
There are a few key ways in which OCD and sensory issues can result in trouble sleeping. One is that people with OCD often have difficulty winding down at night due to their constant worry and racing thoughts. This can make it hard to fall asleep or stay asleep through the night.
Additionally, people with OCD may also have sensitivities to noise, light, and touch that can make it difficult to sleep in a comfortable environment. Finally, many people with OCD engage in rituals or compulsions that take up time and energy, making it harder to get a restful night of sleep.
Problems with school or work performance
There are a few key ways in which OCD and sensory issues can result in problems with school or work performance. One way is that the person may have difficulty concentrating on tasks, due to either intrusive thoughts or the need to perform certain rituals. This can make it hard to complete assignments or stay focused during meetings.
Another issue is that people with OCD often miss important deadlines because they’re too busy with their compulsions. And finally, some people with OCD become so overwhelmed by their symptoms that they’re unable to leave the house, which makes it tough to get to work or school.
Social isolation and withdrawal
OCD and sensory issues often result in social isolation and withdrawal. This is because people with OCD and sensory issues may feel that they are different from others, or that they do not fit in. They may also avoid situations where they may be triggered, such as places with bright lights or loud noises. As a result, they may miss out on important social activities and opportunities
Suicidal thoughts or attempts
Many people with OCD and sensory processing issues have a hard time dealing with suicide. For some, the very thought of suicide is so overwhelming that they can’t even begin to process it. Others may become fixated on the idea, obsessively thinking about it and planning ways to do it. In either case, these individuals are at a higher risk of actually attempting or completing suicide.
The constant fear and anxiety can be unbearable, especially if they feel like they’re not getting any relief from their symptoms. The obsessions and compulsions can take over their life, making it impossible to function normally.
They may feel like they’re a burden to their families and friends, and that everyone would be better off without them. The shame and isolation that come with having these conditions can also contribute to suicidal thoughts.
Substance abuse
There are several ways that OCD and sensory issues can lead to substance abuse. For example, people with OCD may turn to drugs or alcohol in an attempt to self-medicate their symptoms.
Additionally, people with OCD may have difficulty coping with the anxiety and stress caused by their condition, which can lead them to abuse substances as a way of numbing themselves. Finally, people with Sensory Processing Disorder may be more likely to abuse substances as a means of escape from the overwhelming sensations they experience daily.
Eating disorders
Someone with OCD might become obsessed with the idea that they are contaminated by germs. This could lead them to develop rigid rules about what foods they will allow themselves to eat, to avoid contact with potential contaminants. Or someone with OCD might be constantly worried about gaining weight, leading them to severely restrict their intake.
Someone with sensory issues, on the other hand, might have a hard time eating certain foods because of the texture, smell, or taste. For example, someone who is sensitive to smells might avoid eating anything that has a strong odor. Or someone sensitive to textures might only be able to eat soft foods.
Excessive sweating or trembling
Someone with OCD might have a fear of contamination and might excessively wash their hands as a result. This can lead to the hands drying out and cracking, which can cause sweating and trembling.
Similarly, someone with OCD might have a fear of heights and avoid situations where they could fall. This can lead to shaking and sweating when confronted with these situations.
Finally, people with OCD often have difficulty tolerating uncertainty and may spend excessive amounts of time worrying about things that could go wrong. This can also lead to shaking and sweating.
Lightheadedness or dizziness
There are a few ways in which OCD and sensory issues can result in lightheadedness or dizziness. One way is if someone with OCD is constantly obsessing over their thoughts, they may start to feel lightheaded or dizzy from the lack of focus on their surroundings.
Another way is if someone with sensory issues is constantly bombarded with stimuli that they can’t process, they may also start to feel lightheaded or dizzy. Lastly, if someone with both OCD and sensory issues isn’t getting enough sleep or proper nutrition, this can also lead to feeling lightheaded or dizzy.
Stomachaches or headaches
There are a few ways that OCD and sensory issues can result in stomachaches or headaches. One way is if someone with OCD becomes fixated on a certain sensation or object, they may start to feel nauseous or dizzy. For example, if someone is constantly thinking about the smell of garbage, they may start to feel sick to their stomach.
Another way is if someone with OCD is trying to avoid a certain sensation, they may end up feeling tense and anxious, which can lead to headaches. Finally, people with OCD may also have trouble eating or sleeping due to their anxiety, which can also lead to stomachaches or headaches.
Muscle tension or pain
There are many ways in which OCD and sensory issues can result in muscle tension or pain. For example, people with OCD may constantly perform certain rituals or compulsions that require them to use a lot of physical energy. This can lead to muscle tension and pain.
People with OCD may also avoid situations that they fear will trigger their symptoms, which can lead to increased levels of anxiety and stress. This can also contribute to muscle tension and pain. Finally, people with OCD may have difficulty sleeping due to their condition, which can further exacerbate muscle tension and pain.
How Can Therapies Help?
There are many types of therapies that can help manage and overcome OCD and sensory issues. Some of the most common include:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy 
CBT focuses on helping people change their thoughts and behaviors.
One way that CBT may help manage OCD and sensory issues are by helping patients learn how to identify and challenge their negative thoughts and beliefs. For example, someone with OCD may have thought that they must wash their hands 100 times before they can leave the house. This thought creates anxiety and leads to the person engaging in the compulsive behavior of washing their hands.
CBT may also help sensory issues by helping patients desensitize themselves to their triggers. For example, someone with a fear of heights may slowly work up to standing on a stool or balcony over some time. This gradual exposure to the trigger can help the person learn that their fear is unfounded and that they can manage their anxiety.
Exposure And Response Prevention 
ERP helps people manage and overcome OCD and other anxiety disorders. In ERP, people are exposed to their fears in a controlled and safe environment, without engaging in the compulsions or avoidance behaviors that they typically use to cope with their anxiety.
This allows them to practice new coping skills and eventually unlearn their old, maladaptive habits.
There are many different ways to implement ERP, but the basic principles remain the same. The therapist works with the individual to develop a hierarchy of fear-inducing stimuli, starting with those that are least distressing and gradually working up to those that are most distressing. The individual then begins exposure exercises, starting with the least distressing stimulus on the hierarchy.
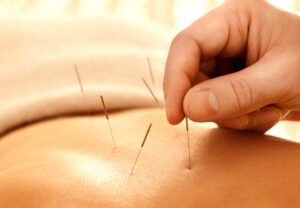
Acupuncture 
This ancient Chinese practice involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. It helps regulate the flow of energy in the body and helps treat OCD and other mental health conditions.
There are a few different ways that acupuncture can help to manage and overcome OCD and sensory issues. First, acupuncture can help to regulate the nervous system. This is important because people with OCD and sensory issues often have a hyperactive or over-stimulated nervous system. Acupuncture can help to calm the mind and ease anxiety and stress by regulating the nervous system.
Second, acupuncture can improve sleep quality. People with OCD and sensory issues often have difficulty sleeping due to their anxiety and stress. Acupuncture can help to improve sleep quality by easing anxiety and stress. Finally, acupuncture can help to improve the quality of life for people with OCD and sensory issues.
Art Therapy 
This type of therapy uses art to help people express their thoughts and feelings.
Art therapy can be extremely helpful for people with OCD and sensory issues. Here are some examples of how art therapy can help manage and overcome OCD and sensory issues:
• Grounding in the present moment: This helps the client focus on the here-and-now, rather than on their obsessions or compulsions. For example, if a client is obsessively worrying about something that happened in the past, the therapist may have them focus on the sensation of their breath going in and out, or on a relaxing image (e.g., a beach scene).
• Increasing self-awareness: Art therapy can help clients to become more aware of their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. For example, if a client is having difficulty expressing their emotions verbally, they may be encouraged to express them through art.
•Building self-esteem and confidence: One of the goals of art therapy is to help clients feel good about themselves and their abilities. For example, if a client creates a piece of art that they are proud of, the therapist may praise their effort and encourage them to share it with others.
If you or someone you know suffers from OCD or sensory issues, art therapy may be a helpful treatment option. It can provide relief from symptoms, and help to increase self-awareness and build self-esteem and confidence.
Mindfulness Therapy 
This is a type of meditation that helps you focus on the present moment and accept your thoughts and feelings without judgment.
One of the ways it does this is by helping the individual to become more aware of their thoughts and feelings, and to understand that they can choose to respond differently to them. For example, if someone with OCD is obsessively thinking about germs, they may be able to use mindfulness techniques to observe their thoughts without getting caught up in them, and eventually learn to let them go.
Similarly, if someone with sensory issues is triggered by certain sounds or textures, they may be able to use mindfulness to observe their reactions without getting overwhelmed or upset, and eventually learn to tolerate these sensations.
Aromatherapy
This involves using essential oils to help promote relaxation and calm. Aromatherapy has long been used as a way to help manage anxiety and stress. The sense of smell is closely linked to the limbic system in the brain, which controls emotions.
Several different essential oils are fruitful for OCD and sensory issues. Some of the most popular include lavender, chamomile, and bergamot.
Each of these oils has its unique scent and benefits. For example, lavender is known for its calming properties, while chamomile can help to reduce anxiety. Bergamot, on the other hand, is known for its ability to boost mood and improve energy levels.
When it comes to using essential oils for OCD and sensory issues, it’s important to find a scent that you enjoy. This will help you to feel more relaxed and comfortable when using them.
How Can Self-Care Tips Help? 
Several self-care tips can help manage and overcome OCD and sensory issues. These include:
- Make your atmosphere clean: A cluttered or dirty environment can be a trigger for OCD and sensory issues. Keeping your surroundings clean and tidy can help to reduce anxiety and stress levels.
- Gardening: like making your atmosphere clean, gardening can also help reduce anxiety and stress levels. Being in nature and surrounded by greenery has been shown to have a calming effect on the mind.
- Eating a balanced diet: Eating a healthy, balanced diet is important for overall mental health. Some specific foods that are beneficial for OCD and sensory issues include omega-rich foods, probiotics, and magnesium-rich foods.
- Start writing: Writing can be a therapeutic way to deal with OCD and sensory issues. It can help to offload some of the negative thoughts and feelings that are going through your head, and can also be a way to track your progress over time.
- Read motivational stories: Reading stories of others who have overcome OCD and sensory issues can be incredibly motivating. It can remind you that recovery is possible, and provide you with some useful tips and strategies to try.
- Find a hobby: Doing something that you enjoy can help to take your mind off of your OCD or sensory issues. It can also give you a sense of accomplishment and pride, which can help boost self-esteem.
These are just some of the self-care tips that can help with OCD and sensory issues. Remember, everyone is different and what works for one person may not work for another. It’s important to find what works for you and stick with it.
Conclusion
OCD and sensory issues are interrelated. However, it is important to be aware of the potential for OCD and sensory symptoms to co-occur. If you or someone you know is struggling with OCD and/or sensory issues, there are many resources available to help.
Don’t wait to get help if you or someone you know is struggling as it may take a toll on your health and life. Remember that life is precious and should not be wasted on OCD and sensory issues. We all deserve to live our best lives possible.