Dementia can be a difficult disease to understand, both for the person who is diagnosed and for their loved ones. It can be hard to know what to expect and how to best support a person with dementia. In this blog post, we will discuss some of the most common symptoms of dementia. This information can help you become more familiar with the disease and better equipped to handle its challenges.
Contents
- 1 What Is Dementia?
- 2 Different Types of Dementia
- 3 Symptoms of Dementia
- 3.1 Memory Loss
- 3.2 Confusion
- 3.3 Difficulty Speaking or Swallowing
- 3.4 Changes in Mood and Behavior
- 3.5 Difficulty With Planning And Problem-Solving
- 3.6 Decline In Physical Abilities
- 3.7 Changes In Mood and Behavior
- 3.8 Difficulty In Communicating
- 3.9 Difficulty In Handling Tasks
- 3.10 Personality Changes
- 3.11 Hallucinations
- 3.12 Incontinence
- 4 Causes of Dementia
- 5 Risk Factors of Dementia
- 6 How Is Dementia Diagnosed?
- 7 How Is Dementia Treated?
- 8 Preventing Dementia
- 9 Conclusion
- 10 A Word From Therapy Mantra
What Is Dementia?
 Dementia is a general term for a decline in mental ability severe enough to interfere with daily life. Memory loss is usually one of the first signs. Dementia affects people of all ages, but it’s most common in older adults. Sometimes this disease also can cause changes in mood and behavior.
Dementia is a general term for a decline in mental ability severe enough to interfere with daily life. Memory loss is usually one of the first signs. Dementia affects people of all ages, but it’s most common in older adults. Sometimes this disease also can cause changes in mood and behavior.
It also can lead to a decline in physical abilities. Sometimes dementia also can cause changes in mood and behavior.
Different Types of Dementia
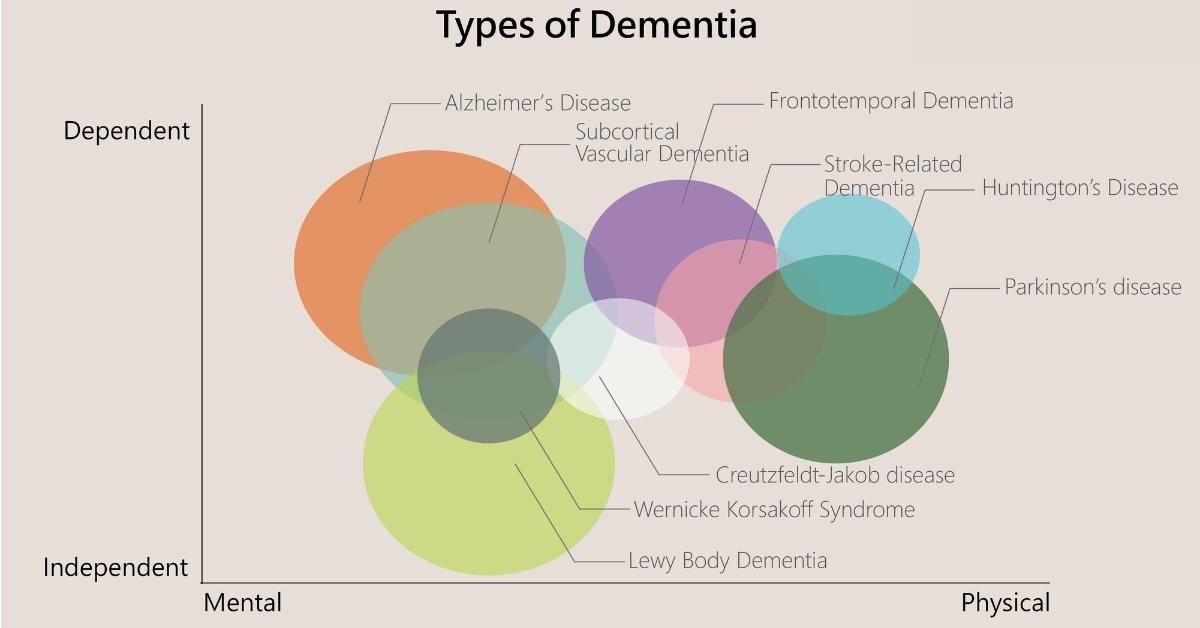
There are many types of dementia, but the most common are Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, and Lewy body dementia.
Alzheimer’s Disease
This is the most common type of dementia. It accounts for 60 to 80 percent of cases. In Alzheimer’s disease, cells in the brain produce a chemical called acetylcholine to die off. This affects memory, thinking skills, and behavior. It also can lead to a decline in physical abilities.
Vascular Dementia
This type of dementia is caused by problems with the blood vessels that supply the brain. It’s the second most common type of dementia, accounting for about 20 percent of cases. In vascular dementia, lack of oxygen or nutrients to the brain can damage cells and cause them to die off. This affects thinking skills and behavior.
Lewy Body Dementia
This type of dementia is caused by abnormal proteins called Lewy bodies that form in nerve cells in the brain. It accounts for about 15 percent of cases. In Lewy body dementia, changes in mood and behavior are often the first signs. Memory loss and thinking skills also may be affected later on.
Symptoms of Dementia
There are many symptoms of dementia, but some of the most common are:
Memory Loss
 This sign also means that a person with dementia may have problems with words, numbers, and concepts. It also can make it hard to follow a conversation or keep track of what’s going on around them. Memory loss is usually the first sign of dementia.
This sign also means that a person with dementia may have problems with words, numbers, and concepts. It also can make it hard to follow a conversation or keep track of what’s going on around them. Memory loss is usually the first sign of dementia.
Confusion
People with dementia may become confused about time, people, places, and what they’re doing. This can lead to agitation and even aggression.
Difficulty Speaking or Swallowing
 In later stages of dementia, people may have difficulty speaking because they can’t find the words they need or they may slur their speech. They also may have difficulty swallowing because of a loss of muscle control.
In later stages of dementia, people may have difficulty speaking because they can’t find the words they need or they may slur their speech. They also may have difficulty swallowing because of a loss of muscle control.
Changes in Mood and Behavior
This is one of the symptoms of dementia. Dementia can cause changes in mood and behavior that range from mild problems such as restlessness to severe behaviors such as yelling, screaming, or violence. These changes often are the first signs that something is wrong.
Difficulty With Planning And Problem-Solving
 This is one of the symptoms of dementia. People with dementia may have trouble coming up with ideas, planning projects, or solving problems.
This is one of the symptoms of dementia. People with dementia may have trouble coming up with ideas, planning projects, or solving problems.
Decline In Physical Abilities
Dementia can lead to a decline in physical abilities over time. This includes problems with walking, getting dressed, bathing, and using the toilet. This also can lead to a higher risk of falling.
Changes In Mood and Behavior
 People with dementia may experience changes in mood, such as depression, anxiety, or irritability. They also may act out of character or be difficult to manage. Sometimes this also can lead to a decline in physical abilities.
People with dementia may experience changes in mood, such as depression, anxiety, or irritability. They also may act out of character or be difficult to manage. Sometimes this also can lead to a decline in physical abilities.
Difficulty In Communicating
This is one of the earliest signs of dementia. People with the disease may have trouble finding the right words, understanding what others are saying, or writing. It also can make it hard to follow a conversation or keep track of what’s going on around them.
Difficulty In Handling Tasks
 This is one of the later signs of dementia. People with the disease may have trouble completing tasks they normally would be able to do, like getting dressed or cooking a meal. They also may need help to remember how to do things they’ve done before. Sometimes this leads to a decline in physical abilities.
This is one of the later signs of dementia. People with the disease may have trouble completing tasks they normally would be able to do, like getting dressed or cooking a meal. They also may need help to remember how to do things they’ve done before. Sometimes this leads to a decline in physical abilities.
Personality Changes
People with dementia may become more withdrawn, quiet, or passive. They also may become suspicious, paranoid, or delusional. In some cases, they may act out of character and be difficult to manage. Sometimes they may also have a decline in physical abilities.
Hallucinations
 This one sign is also common in people with Alzheimer’s disease. People with dementia may see, hear, smell, or feel things that aren’t there.
This one sign is also common in people with Alzheimer’s disease. People with dementia may see, hear, smell, or feel things that aren’t there.
Incontinence
People with dementia may have trouble controlling their bladder or bowel movements. This can lead to accidents and a need for more help with personal care. Sometimes this also can lead to a decline in physical abilities.
Causes of Dementia
There can be many causes of dementia, including:
Medical Conditions
Sometimes changes in the brain that lead to dementia are caused by a medical condition, such as:
- stroke
- multi-infarct dementia
- Huntington’s disease
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease
Infections
Certain infections can cause changes in the brain that lead to dementia. These include:
- Lyme disease
- tuberculosis
Brain Diseases And Injury
Dementia can also be caused by certain diseases of the brain or injuries to the head. For example, Alzheimer’s is a type of dementia that is caused by changes in the brain. It can also be caused by a head injury, like a concussion.
Chemical And Environmental Agents
Dementia also can be caused by exposure to certain chemicals or environmental agents, such as:
- lead
- arsenic
- carbon monoxide
- drugs and alcohol abuse.
Risk Factors of Dementia
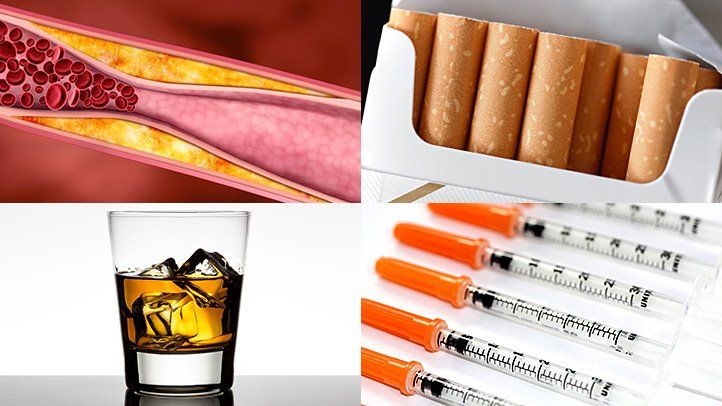
There are many risk factors for dementia, including:
Age
The older a person gets, the greater their risk for dementia. This is because the brain naturally changes with age and these changes can lead to dementia.
Gender
Women are more likely than men to develop Alzheimer’s disease, which is the most common type of dementia.
Genetics
Some diseases that cause dementia, like Huntington’s disease and Down syndrome, are passed down in families through genes. This means that people who have a family history of these diseases are at greater risk for developing dementia.
Smoking
People who smoke are twice as likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease as those who don’t smoke. This may be because smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of strokes, which can lead to dementia.
High Blood Pressure
People who have high blood pressure are at greater risk for developing vascular dementia, which is the second most common type of dementia. This is because high blood pressure can damage blood vessels in the brain and reduce the amount of oxygen that gets to the brain.
Diabetes
People with diabetes are also at greater risk for developing vascular dementia. This is because diabetes can damage blood vessels in many parts of the body, including the brain.
Depression
Depression may increase a person’s risk for dementia. This is because depression can cause changes in the brain that lead to memory problems and confusion.
How Is Dementia Diagnosed?

There is no one test to diagnose dementia. A doctor will do a physical exam and ask about the person’s medical history and symptoms. They also may order tests such as:
Blood Tests
These tests can help rule out other causes of the person’s symptoms. These tests may include:
- tests to measure the level of certain chemicals in the blood
- tests to check for infections
Brain Imaging Tests
These tests can help show changes in the brain that may be causing dementia. This includes:
- CT scan
- MRI scan
- PET scan.
EEG
An EEG measures electrical activity in the brain. This test can help doctors determine if someone has Lewy body dementia. Sometimes it can also help diagnose Alzheimer’s disease.
How Is Dementia Treated?

There is no one treatment for dementia. The goal of treatment is to help the person maintain their quality of life and independence as long as possible. This may include:
Medications
There are many medications that can help treat the symptoms of dementia. These medications include:
- drugs to help with memory problems
- drugs to help with confusion and disorientation
- medications to help with behavior changes
Non-Medical Therapies
There are many non-medical therapies that can help people with dementia. These therapies may include:
- occupational therapy
- speech therapy
- physical therapy.
Counseling
This can be one of the most important therapies for people with dementia. Counseling can help them deal with the changes in their life and the stress of having a disease. It also can help caregivers learn how to best care for someone with dementia.
Support Groups
There are many support groups available for people with dementia and their caregivers. These groups can offer emotional support, information, and resources.
Preventing Dementia

There is no sure way to prevent dementia, but there are things you can do to lower your risk:
Stay Physically Active
Physical activity has been shown to help protect against cognitive decline and memory loss. It also can improve mood and overall well-being.
Maintain Healthy Diet
A healthy diet is important for keeping your mind and body healthy. Eating foods that are high in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, may help reduce your risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
Limit Your Alcohol Intake
Too much alcohol can damage the brain over time and increase your risk of developing dementia.
Quit Smoking
Smoking has been linked to a number of health problems, including cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease.
Stay Social And Engaged
Social interaction and engagement have been shown to help protect against cognitive decline. Participating in activities that you enjoy can help keep your mind active and healthy.
Keep Your Mind Active
Challenging your brain with new activities and puzzles can help keep it healthy and functioning well into old age. Sometimes it can even help delay the onset of dementia.
Conclusion
Dementia is one of the most common diseases among the elderly. It can be difficult to deal with both the person with dementia and their caregivers. There are many different treatments available to help make life easier for everyone involved.
In conclusion, there are many things you can do to help lower your risk of developing dementia. While there is no sure way to prevent it, following these tips can help keep your mind and body healthy. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of dementia, be sure to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
A Word From Therapy Mantra
Your mental health — your psychological, emotional, and social well-being — has an impact on every aspect of your life. Positive mental health essentially allows you to effectively deal with life’s everyday challenges.
Also, at Therapy Care, we have a team of therapists who provide affordable online therapy to assist you with issues such as depression, anxiety, stress, relationship, OCD, LGBTQ, and PTSD. You can take our mental health test. You can also book a free therapy or download our free Android or iOS app.


