If you are someone who struggles with ADHD, you may also find that you struggle with anger management. It can be difficult to deal with your emotions when they are all bottled up inside of you. In this blog post, we will discuss some of the best ways to deal with ADHD and anger management. We will also provide some helpful tips for managing your anger in a healthy way.
Contents
Understanding ADHD And Anger
 ADHD is a medical condition that affects millions of children and adults worldwide. The symptoms of ADHD can include impulsivity, inattention, and hyperactivity. While most people with ADHD do not have anger management problems, some may struggle with controlling their temper.ADHD and anger management problems often go hand-in-hand. One study found that children with ADHD were more likely to have problems with anger than kids without ADHD. Anger is a common symptom of ADHD, and it can be one of the most difficult symptoms to manage.
ADHD is a medical condition that affects millions of children and adults worldwide. The symptoms of ADHD can include impulsivity, inattention, and hyperactivity. While most people with ADHD do not have anger management problems, some may struggle with controlling their temper.ADHD and anger management problems often go hand-in-hand. One study found that children with ADHD were more likely to have problems with anger than kids without ADHD. Anger is a common symptom of ADHD, and it can be one of the most difficult symptoms to manage.
Link Between ADHD And Anger
The connection between ADHD and anger is well-documented. In fact, one study found that people with ADHD are more likely to experience anger and aggression than those without the disorder. The link between ADHD and anger may be due to a number of factors, including the impulsivity and hyperactivity characteristic of ADHD. Additionally, people with ADHD often have difficulty regulating their emotions, which can lead to outbursts of anger. While it’s normal for everyone to experience anger from time to time, people with ADHD may find that their anger is more intense and difficult to control.
Common symptoms Of ADHD and Anger
There are a number of symptoms that are associated with ADHD and anger. These include:
- feeling easily frustrated or overwhelmed
- having difficulty concentrating or staying focused on tasks
- feeling restlessness or fidgety
- acting impulsively without thinking things through
- having difficulty controlling your temper or getting easily angry
These symptoms can often lead to problems in both schools and at home. If you are struggling with ADHD and anger, it is important to seek professional help. A therapist can work with you to develop coping skills and strategies to better manage your symptoms.
Consequences
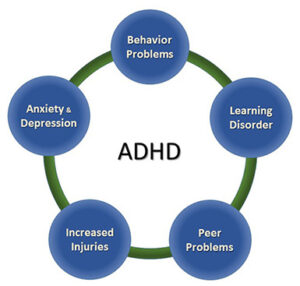
If left untreated, ADHD and anger can lead to a number of problems. These include:
Poor performance in school
ADHD can make it difficult for children to focus and pay attention in class, which can lead to lower grades. ADHD can make it hard for children to socialize and interact with others. This can lead to difficulty making and keeping friends. For example, a child with ADHD may have trouble following rules and instructions, which can result in getting into fights with other kids.
ADHD can make it hard to start and finish tasks. This can lead to problems at school, such as not completing homework or chores. Poor grades and a lack of friends can lead to feelings of isolation and low self-esteem.
The trouble with the law
ADHD may increase the risk of getting into trouble with the law. For example, a person with ADHD may be more likely to speed or drive recklessly. Untreated ADHD can also lead to risky behaviors, such as drug use. ADHD and anger may lead to disruptive behavior, such as fighting or property destruction.
Problems at home
ADHD can lead to problems at home, such as not following rules or helping with chores. This can cause arguments and conflict between parents and siblings. This can lead to conflict between parents and siblings. For example, a child with ADHD may have trouble completing chores or homework. For example, a child with ADHD may have difficulty following rules and instructions, which can result in arguments with parents or other family members. A child with ADHD may also act impulsively, which can lead to accidents or injuries.
Problems with relationships
ADHD and anger can make it hard to maintain friendships and romantic relationships. For example, people with ADHD may become easily bored in conversations, interrupt others often, or speak without thinking first. This can make it difficult for others to understand them and can lead to arguments. In addition, people with ADHD may have trouble keeping promises. This can also damage relationships. People with ADHD may need to be more understanding and patient with themselves and others.
Acting out in aggressive or violent ways
Many people with ADHD have difficulty managing their anger. This can lead to them acting out in aggressive or violent ways. If you have ADHD and find yourself getting angry easily, it’s important to find healthy ways to deal with your anger. Otherwise, you may end up hurting yourself or others.
Experiencing anxiety or depression
Another common consequence of ADHD is anxiety or depression. This can make it even harder to deal with your anger in a healthy way. For instance, you may find yourself getting more easily irritated or frustrated than usual. Or, you may have a hard time “letting go” of your anger after an argument with someone. If you’re struggling with anxiety or depression, it’s important to get help from a mental health professional.
Trouble sleeping
People with ADHD may have trouble falling asleep or staying asleep. This can make them feel tired during the day, which can lead to irritability and frustration. For example, if you have trouble falling asleep, you may be irritable and short-tempered the next day.
Lack of focus
People with ADHD often have trouble focusing on tasks, which can make it difficult to complete projects or meet deadlines. This can lead to frustration and feeling overwhelmed. For instance, you may start cleaning your house but get sidetracked and never finish. Or you may begin a work project but get distracted and have to start over several times.
Procrastination
People with ADHD often procrastinate or put off tasks because they’re overwhelmed by the amount of work that needs to be done. This can lead to feelings of frustration and anger. For instance, if you’re trying to get a project done but keep getting distracted, you may start to feel angry at yourself for not being able to focus.
Impulsivity
People with ADHD may act on impulse, which can lead to problems at work, school, or in relationships. For example, you may say something without thinking first, or you may have trouble controlling your temper.
Self-harming behaviors
If you’re dealing with ADHD and anger, it’s important to be aware of the possibility of self-harming behaviors. These can include anything from cutting or burning oneself to pulling out one’s hair or picking at skin. While these behaviors may seem minor, they can actually be quite dangerous and should not be ignored. If you notice any of these behaviors in yourself or someone you know, it’s important to get help from a professional right away.
It’s also important to understand that self-harming behavior is often a way of numbing emotional pain. All of these problems can lead to frustration and anger. Additionally, people with ADHD may act impulsively without thinking about the consequences of their actions. ADHD can be frustrating for both the person with the disorder and the people around them. If you have ADHD, there are things you can do to manage your symptoms and live a productive, happy life.
Treatment
 There are many ways to treat ADHD, but there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Some people with ADHD need medication to help them focus and control their impulsivity. Others may benefit from therapy, support groups, or lifestyle changes.
There are many ways to treat ADHD, but there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Some people with ADHD need medication to help them focus and control their impulsivity. Others may benefit from therapy, support groups, or lifestyle changes.
Seek professional help: If you or your child is struggling with ADHD, it’s important to seek professional help. A mental health professional can evaluate symptoms and make a diagnosis. They can also provide treatment recommendations.
Therapy
Anger management can help you learn to control your temper and react more calmly in frustrating situations. Therapy which is included:
Cognitive behavioral therapy: This type of therapy can help you identify and change negative thought patterns that contribute to angry outbursts. It includes learning to recognize and manage triggers, controlling your responses to anger, and developing coping and problem-solving skills.
Child-centered play therapy: Play therapy is a type of psychotherapy that uses play to help children express their emotions and address behavioral issues. Play therapy can be used with children of all ages, but it is particularly beneficial for younger children who may not have the verbal skills to express themselves.
Family therapy: Family therapy can be helpful if your family dynamic is contributing to your anger. Family therapy can help you improve communication and problem-solving skills, as well as develop a more positive relationship with your family members.
Group therapy: It can be an effective way to help manage anger. In group therapy, you will learn about different techniques for managing anger and share your experiences with others who are struggling with similar issues.
Interpersonal therapy: Interpersonal therapy focuses on your relationships and how they may be affecting your anger. This type of therapy can help you learn to communicate better, set boundaries, and resolve conflict in a healthy way.
Biofeedback
Biofeedback is a treatment option that can be used to help people with ADHD manage their anger. It involves using sensors to measure things like heart rate and skin temperature. The goal of biofeedback is to help the person become more aware of their body’s response to stressors so that they can learn to control them.
Medication
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage ADHD symptoms or other conditions that may be contributing to anger. It can be a helpful part of treatment, but it’s important to work with a mental health professional to determine if it’s the right option for you. However, it’s important to note that medication should not be used as a sole treatment for anger. It should be used in combination with therapy and other treatment options.
Parental training
Anger management for parents of children with ADHD can be difficult. Many times, the children acting out is a result of their ADHD symptoms. Parental training is an important part of helping a child with ADHD manage their anger. By providing structure and teaching coping skills, parents can help their children feel more in control and less frustrated.
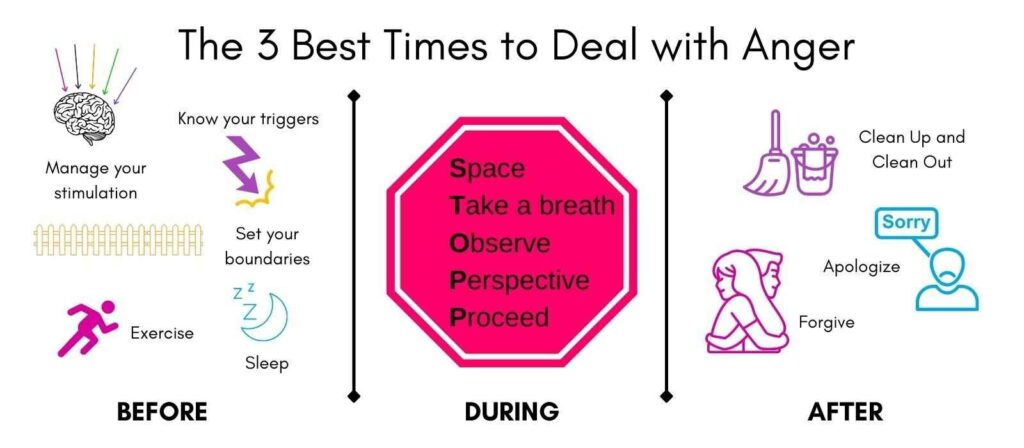
Self Help Tips
Here are a few tips to help you manage your anger:
- Identify your triggers. What sets off your anger? Once you know what your triggers are, you can try to avoid them or be prepared for them.
- Communicate with the people around you. Let the people in your life know that you’re working on anger management and that you may need their help.
- Exercise can help you release some of the pent-up energy that can contribute to anger.
- Relaxation techniques: Relaxation exercises, such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation, can help reduce stress and anxiety, which can trigger anger.
- Learning how to manage stress in a healthy way can also help reduce the intensity and frequency of your anger.
Many people with ADHD struggle with anger, and it can be a real challenge to deal with. However, there are some things you can do to help manage your anger and make life a little easier.
Conclusion
It may be concluded that ADHD can lead to problems with anger management. However, there are ways to help manage this difficult symptom. With the proper diagnosis and treatment, people with ADHD can learn how to better control their emotions and reactions. If you or someone you know has ADHD and is struggling with anger management, please seek professional help.
If you need more help or have any questions, don’t hesitate to reach out to Therapy Mantra. We have a whole team of experienced therapists and psychiatrists who would be glad to assist you. Contact us quickly to learn about everything we can do for you. You may also make an online therapy session or download our free Android or iOS app.