Critical Incident Stress is a psychological response that can occur after exposure to a traumatic event. This may include events such as natural disasters, terrorist attacks, serious accidents, or assaults.
Many people who are exposed to such events do not develop Critical Incident Stress. In this article, we will explore what Critical Incident Stress is, the symptoms and effects, how to cope, and where to seek help.
Contents
Understanding Critical Incident Stress

A critical incident is any event that overwhelms your usual coping mechanisms and leaves you feeling stressed, anxious, or traumatized. This can be a one-off event such as a car accident or assault, but it can also be something that happens repeatedly, such as being in a violent relationship.
There are three main types of Critical Incidents:
- Personal Trauma: such as physical or sexual assault, serious accidents or injuries, death of a loved one.
- Public Trauma: such as terrorist attacks, natural disasters, mass shootings.
- Workplace Trauma: such as accidents at work, witnessing someone being seriously injured or killed at work.
Critical Incident Stress Disorder
Critical Incident Stress Disorder (CISD) is a condition that can develop after exposure to a traumatic event. It is characterized by symptoms such as intrusive thoughts, flashbacks, avoidance, and hyperarousal. CISD can lead to problems with work, relationships, and social life.
CISD Vs. PTSD
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a condition that can develop after exposure to a traumatic event. It is characterized by symptoms such as intrusive thoughts, flashbacks, avoidance, and hyperarousal. PTSD can lead to problems with work, relationships, and social life.
There are some key differences between CISD and PTSD.
CISD:
- Is a short-term reaction to a critical incident, while PTSD is a long-term reaction.
- Symptoms typically resolve within six months, while PTSD symptoms can last for years.
- Does not require treatment, while PTSD often requires treatment.
Degrees of CISD
There are three degrees of CISD, depending on the severity of the symptoms:
- Mild CISD: Symptoms last for a few days to a week and do not significantly interfere with work or social life.
- Moderate CISD: Symptoms last for more than a week and may interfere with work or social life.
- Severe CISD: Symptoms are disabling and significantly interfere with work and social life.
Symptoms of CISD
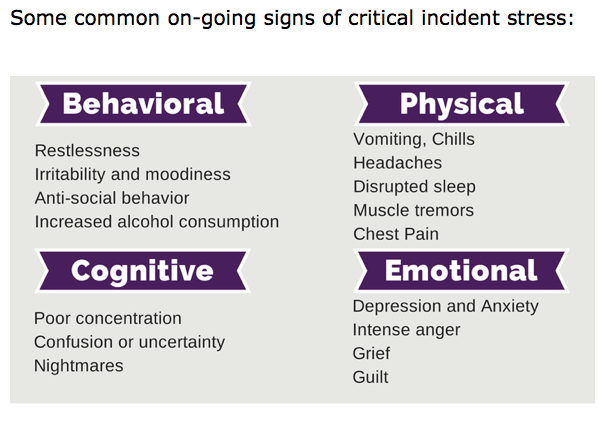
The symptoms of CISD can be divided into four categories:
Flashbacks: Flashbacks are vivid memories of the event that come back unexpectedly and can feel like you are reliving it.
Intrusive thoughts: These are unwanted, intrusive thoughts about the event that cause distress. They can include images, sounds, and smells that are related to the event.
Avoidance: People with CISD may start to avoid anything that reminds them of the event. This can include people, places, activities, and thoughts.
Hyperarousal: Hyperarousal is a state of being constantly on edge and feeling like danger is imminent. It can lead to problems such as difficulty sleeping, irritability, and outbursts of anger.
Causes of CISD
The causes of CISD are not fully understood, but it is thought to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. One theory is that CISD is caused by changes in the way the brain processes trauma. This may be due to a combination of genetic vulnerability and exposure to traumatic events.
Risk Factors of CISD
There are several risk factors for developing CISD, such as:
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop CISD than men.
- Age: Young people are more likely to develop CISD than older adults.
- Lack of social support: People who lack social support are more likely to develop CISD.
- History of trauma or abuse: People who have a history of trauma or abuse are more likely to develop CISD.
- Exposure to multiple traumatic events: People who have been exposed to multiple traumatic events are at a higher risk of developing CISD.
- Having a pre-existing mental health condition: People with mental health conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or anxiety disorder are more likely to develop CISD after exposure to a traumatic event.
Living With CISD
CISD can have a significant impact on all aspects of a person’s life. It can lead to problems with work, relationships, and social life.
Ill-effects on Relationships
CISD can cause problems in relationships such as communication difficulties, conflict, and intimacy issues.
- Conflict: People with CISD may argue more with their partners. This can be due to difficulty communicating, as well as hyperarousal and irritability.
- Communication difficulties: People with CISD may have difficulty communicating with their partners about the event. This can lead to misunderstandings and conflict.
- Intimacy issues: People with CISD may have difficulty forming and maintaining intimate relationships. This may be due to avoidance of social activities, flashbacks, and intrusive thoughts.
Ill-effects on Work
CISD can cause problems with work such as absenteeism, lost productivity, and job satisfaction.
- Absenteeism: People with CISD may take more time off work. This can be due to difficulty concentrating, flashbacks, and intrusive thoughts.
- Lost productivity: People with CISD may have difficulty concentrating at work. This can lead to lost productivity and errors.
- Job satisfaction: People with CISD may be less satisfied with their job. This can be due to lost productivity and difficulty communicating with co-workers.
Ill-effects on Social Life
CISD can cause problems with social life such as avoidance of social activities, isolation, and difficulty forming and maintaining relationships.
- Isolation: People with CISD may become isolated from friends and family. This can be due to avoidance of social activities and intimacy issues.
- Avoidance of social activities: People with CISD may avoid social activities. This can be due to flashbacks, intrusive thoughts, and hyperarousal.
- Difficulty forming and maintaining relationships: People with CISD may have difficulty forming and maintaining relationships. This can be due to avoidance of social activities, intrusive thoughts, and hyperarousal.
NOTE: People with CISD may also find it difficult to cope on their own and may need help from a professional therapist.
Coping With CISD
Several things can be done to cope with CISD.
Self-help Tips

Several self-help tips can be useful for people with CISD.
Avoid watching or reading about traumatic events: People with CISD may find it helpful to avoid watching or reading about traumatic events. This can help to reduce the amount of trauma they experience.
Stay connected to friends and family: People with CISD may find it helpful to stay connected to friends and family. This can provide social support and reduce feelings of isolation.
Talk to someone who understands: People with CISD may find it helpful to talk to someone who understands. This can be a friend, family member, therapist, or support group.
Maintain a healthy lifestyle: People with CISD may find it helpful to maintain a healthy lifestyle. This can help to reduce stress and improve overall health. Some lifestyle tips include:
- Maintain a healthy diet
- Exercise regularly
- Get enough sleep
- Reduce alcohol and drug use
Get professional help: People with CISD may find it helpful to get professional help. This can be from a therapist, support group, or medication.
Self-help Techniques
Several self-help techniques can be useful for people with CISD.
- Meditation: Meditation can help to focus the mind and reduce stress.
- Mindfulness: Mindfulness is a technique that can help people to focus on the present moment and reduce stress.
- Self-care: Self-care is important for people with CISD. This includes activities such as getting enough sleep, exercise, and relaxation.
- Relaxation techniques: Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing and progressive muscle relaxation can help to reduce stress.
Self-help Tools
Several self-help tools can be useful for people with CISD.
- Yoga: Yoga is a form of exercise that can help to improve flexibility, strength, and relaxation.
- Journaling: Journaling can help express thoughts and feelings, as well as track progress.
- Tai chi: Tai chi is a martial art that can help to improve balance and flexibility, as well as reduce stress.
- Therapy Dogs: Therapy dogs can help provide social support and reduce stress.
- Support Groups: Support groups can help provide social support and share information.
Talking To Professional

If you are struggling to cope with CISD, it is important to talk to a professional. This can be a therapist, support group, or doctor. They can help you to understand your symptoms and develop coping strategies. Furthermore, therapists can provide support and guidance, as well as offer treatment options.
Treatment Options
Several treatment options can be helpful for people with CISD.
- Therapy: Therapy is a common treatment for CISD. It can help to reduce symptoms, improve coping skills, and provide support.
- Medication: Medication may be prescribed to help reduce symptoms of CISD.
Therapies
Several therapies can be helpful for people with CISD.
Music Therapy: Music therapy can help to reduce stress and improve mood.
Art Therapy: Art therapy can help people to express their thoughts and feelings, as well as improve self-esteem.
Exposure Therapy: Exposure therapy is a type of therapy that helps people to confront their fears. It can help reduce symptoms of CISD.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy is a type of therapy that helps to change the way a person thinks and behaves. It can help reduce symptoms of CISD.
Trauma-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy: Trauma-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy is a type of therapy that focuses on the trauma a person has experienced. It can help reduce symptoms of CISD.
Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing: Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing is a type of therapy that uses eye movements to help reduce the stress associated with a traumatic event.
Group therapy: Group therapy is a type of therapy that takes place in a group setting. It can help reduce symptoms of CISD and provide social support.
Family therapy: Family therapy is a type of therapy that involves family members. It can help improve communication and relationships within the family.
Medication
Several medications can be helpful for people with CISD.
Anxiolytics: Anxiolytics can help to reduce symptoms of anxiety.
Tranquilizers: Tranquilizers can help to reduce symptoms of stress.
PTSD medications: PTSD medications can help to reduce symptoms of PTSD.
Antidepressants: Antidepressants can help to reduce symptoms of depression.
Anti-anxiety medications: Anti-anxiety medications can help to reduce symptoms of anxiety.
Case Study
Here is an example of a case study on CISD.
A 34-year-old woman was referred to therapy after experiencing symptoms of CISD following a traumatic event. She had difficulty sleeping, felt overwhelmed, and exhibited signs of avoidance.
After several sessions of therapy, she reported that her symptoms had improved significantly. She was able to sleep better, felt more able to cope, and had stopped avoiding anything that reminded her of the event.
Helping Someone With CISD
If you know someone who is struggling with CISD, there are several things you can do to help.
Listen: One of the most important things you can do is to listen. Allow them to share their experiences and feelings without judgment.
Understand: Be understanding of the person’s symptoms and be there for them when they need you.
Support: Offer support and encouragement. Let them know that they are not alone and that you are there for them.
Resources: Provide resources, such as books, articles, or website information. This can help them to learn more about CISD and how to cope with it.
Support their coping strategies: If someone is struggling with CISD, support their coping strategies. This may include things like relaxation techniques and journaling.
Encourage them to seek professional help: If someone is struggling with CISD, it is important for them to seek professional help. This can be in the form of therapy, medication, or both.
Hearing From CISD Experts
There are several experts on CISD who can provide helpful information.
Dr. Peter A. Levine: Dr. Peter A. Levine is a therapist who specializes in trauma and stress. He has written several books on CISD, including “Waking the Tiger.”
Dr. Bessel van der Kolk: Dr. Bessel van der Kolk is a psychiatrist who specializes in trauma. He has written several books on CISD, including “The Body Keeps the Score.”
There are several things that experts say about CISD.
CISD:
- Is a real thing: CISD is a real thing and it can be debilitating.
- Can be treated: CISD can be treated with therapy, medication, and self-help techniques.
- Affects the whole person: CISD affects the whole person, including their physical, emotional, and social wellbeing.
Critical Incident Stress Debriefing
A critical incident stress debriefing (CISD) is a type of therapy that can be helpful for people with CISD.
During a CISD, participants will discuss the traumatic event that has occurred. This can help to reduce symptoms of CISD and provide support.
Brain activity during CISD
The brain activity during a CISD is different than when a person is not experiencing CISD.
During a CISD, the brain goes into a state of hyperarousal. This means that it is in a heightened state and is ready to react to danger.
This can be helpful for people who have experienced a traumatic event. It can help them to understand their symptoms and develop coping strategies.
Brain Activity During CISD
Some research suggests that brain activity may be different during a critical incident stress debriefing.
One study found that people who participated in a CISD had increased activity in the frontal lobe, which is responsible for decision-making and problem-solving.
Another study found that people who participated in a CISD had decreased activity in the amygdala, which is responsible for fear and anxiety.
CISD can affect the brain in several ways. CISD can cause changes in:
- Gene expression: CISD can cause changes in gene expression, which may lead to long-term effects.
- The structure of the brain: CISD can cause changes in the structure of the brain, which can lead to long-term effects.
- In brain activity: CISD can cause changes in brain activity, which can lead to symptoms such as intrusive thoughts and hyperarousal.
Books on CISD
There are several books available on CISD.
“Waking the Tiger: Healing Trauma” by Peter A. Levine
“The Body Keeps the Score: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of Trauma” by Bessel van der Kolk
“Trauma-Informed Yoga Therapy: Theory and Practice for Safe and Effective Treatment” by David Emerson and Elizabeth Hopper
Conclusion
CISD can be a difficult experience, but there are many resources and treatments available to help. If you or someone you know is struggling with CISD, reach out for help. Talk to a professional about your symptoms and develop a plan to cope.
Furthermore, self-care is important for managing CISD. Be sure to take care of yourself emotionally and physically. Lastly, remember that you are not alone in this experience. Many people understand what you are going through and are here to help.
A Word From Therapy Mantra
Your mental health — Your psychological, emotional, and social well-being — has an impact on every aspect of your life. Positive mental health essentially allows you to effectively deal with life’s everyday challenges.
At TherapyMantra, we have a team of therapists who provide affordable online therapy to assist you with issues such as depression, anxiety, stress, workplace Issues, addiction, relationship, OCD, LGBTQ, and PTSD. You can book a free therapy or download our free Android or iOS app.


