We have all heard of the term repression and may even know what it means. But how many of us know about memory recovery and repression psychology? This is a relatively new area of study that is gaining traction as more and more people are showing interest in it.
In this blog post, we will explore what repression is, the link between memory recovery and repression psychology, and what you need to take care of if you decide to undergo memory recovery therapy.
Contents
Memorizing Memory
We all have memories. They can be happy, sad, embarrassing, or traumatic. But what are they? Memory is the ability to store and recall information. It is a mental process that allows us to keep track of past events and experiences.
Types of Memory
There are three main types of memory: sensory, short-term, and long-term.
Sensory memory: Sensory memory is the ability to remember information that was perceived through the senses, such as sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch. This type of memory lasts for a very short time and usually disappears within seconds or minutes.
Short-term memory: Short-term memory is the ability to remember information for a brief period of time, usually less than 30 minutes. This type of memory helps remember things that are just happening or you recently learned.
Long-term memory: Long-term memory is the ability to remember information for a long period of time, sometimes indefinitely. This type of memory helps store information that is important and you need to remember for a later date.
The Seat of Memory
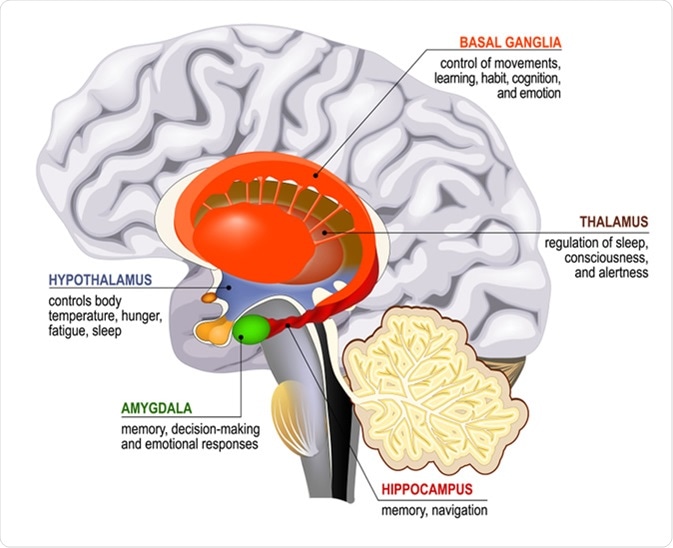
 The human brain is made up of billions of cells called neurons. Each neuron has the ability to form connections with other neurons. These connections are what allow us to store and remember information.
The human brain is made up of billions of cells called neurons. Each neuron has the ability to form connections with other neurons. These connections are what allow us to store and remember information.
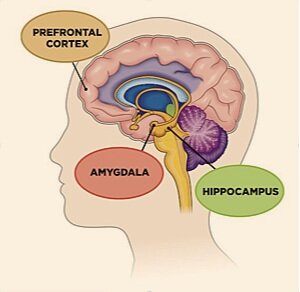
Different parts of the brain are responsible for different types of memory. The hippocampus is responsible for long-term memory, while the cortex is responsible for short-term memory.
- Hippocampus: The hippocampus is a small, curved structure in the brain that is responsible for long-term memory. This part of the brain helps to store memories for a long period of time and also helps with retrieving them later on.
- Cortex: The cortex is the largest part of the human brain. It is responsible for short-term memory. This part of the brain helps to store information for a brief period of time and also helps with retrieving it later on.
Understanding Repression
Repression is a psychological defense mechanism that involves pushing traumatic memories and thoughts deep into the unconscious mind in an attempt to forget them.
What Is Repression Psychology?
Repression psychology is the study of how repression affects thoughts, feelings, and behavior. It is a relatively new field of study that has been gaining traction in recent years.
History And Development
The study of repression and memory recovery dates back to the late 1800s. It was when Sigmund Freud first gave the concept of repression. However, it was not until the 1950s that researchers began to explore the link between repression and memory loss.
Types Of Repression
There are three main types of repression:
Repressive Desensitization: This type of repression occurs when people become desensitized to traumatic memories or thoughts over time.
Example: A soldier who has seen combat may eventually become desensitized to the violence and stop feeling emotional pain or distress.
Intentional Repression: This type of repression occurs when people consciously push traumatic memories and thoughts out of their minds.
Example: A person who was sexually abused as a child may consciously block out the memories of the abuse to avoid dealing with the pain and trauma.
Unintentional Repression: This type of repression occurs when people are unable to remember traumatic memories or thoughts due to amnesia or memory loss.
Example: A person who has suffered a traumatic brain injury may lose the ability to remember certain events due to damage to the brain.
Causes Of Repression
There are many different causes of repression, but some of the most common include:
Traumatic Experiences: Traumatic experiences are one of the main causes of repression. Many people repress memories of traumatic events to avoid dealing with the pain and trauma.
Example: A person who has been raped may repress the memories of the attack to avoid feeling the pain and humiliation.
Emotional Pain: Emotional pain can also be a major cause of repression. Many people repress painful memories or thoughts to avoid feeling the pain and distress.
Example: A person who has been divorced may repress memories of the failed relationship to avoid feeling sad and hurt.
Guilt And Shame: Guilt and shame can also be major causes of repression. Many people repress memories or thoughts that make them feel guilty or ashamed to avoid feeling bad about themselves.
Example: A person who has lied to their friends may repress the memory of the lie to avoid feeling guilty and ashamed.
Lack Of Support: People who do not have a support system are more likely to repress traumatic memories.
Example: A woman who is assaulted by her husband may be too afraid to tell anyone about the assault because she does not have anyone to turn to for help.
Fear Of Punishment: People who face the fear of punishment or ridicule for their thoughts and feelings are more likely to repress them.
Example: A child who is sexually abused by a family member may be too scared to tell anyone about the abuse because he is afraid of being punished.
Repression As a Defense Mechanism
Repression is a defense mechanism that helps people to cope with traumatic memories and thoughts. It allows people to avoid dealing with the pain and trauma associated with these memories.
To understand how repression works, we need to take a look at the three stages of memory: acquisition, retention, and retrieval.
- Acquisition: This is the stage where information is first processed and stored in the brain.
- Retention: This is the stage where information is present in the brain for some time.
- Retrieval: This is the stage where one retrieves information from the memory.
When people experience a traumatic event, the memories of the event are usually stored in the retention stage. The memories may stay there for a few days, weeks, or months, but eventually, they will be forgotten and moved to the retrieval stage.
However, if people do not have a support system, they are more likely to repress these traumatic memories. This means that the memories will not be forgotten, but they will be absent from the person’s consciousness.
The memories will be present in the brain, but the person will not be able to remember them or access them consciously. This is why repression is often called a “subconscious” defense mechanism.
Rising of Repressed Memories
When people repress traumatic memories, they are not deleting the memories from their brains. The memories are still there, but they are not under the cognizance of the person’s conscious mind.
This is why people who have repressed memories often find that they suddenly remember them a few years later. The memories may pop up out of nowhere, or the person may experience triggering/rising of memories from the traumatic event.
The memories may be unclear or fragmented, but they will still be recognizable. Once the person remembers the memory, they may choose to deal with it or ignore it. But, most importantly, they have now regained control over their memories.
Effects Of Repression
Repression can have several negative effects on thoughts, emotions, and behavior.
Emotional Effects: Repression can cause a person to feel numb or disconnected from their emotions.
Example: A woman who was sexually assaulted by her father may feel emotionally numb and disconnected from her feelings.
Mental Effects: Repression can cause a person to have problems with thinking and concentrating.
Example: A man who was sexually assaulted by his brother may have problems with thinking and concentrating.
Behavioral Effects: Repression can also lead to behavioral problems.
Example: A man who was sexually abused by his father may start to act out aggressively or become a substance abuser.
Cognitive Effects: Repression can also lead to cognitive problems.
Example: A woman who was sexually assaulted by her father may have difficulty thinking logically and making decisions.
Decoding The Link Between Memory Recovery And Repressed Psychology
So what is the link between memory recovery and repression psychology?
However, there is no right or wrong way to do this. Some people choose to deal with their memories head-on, while others may prefer to take a more gradual approach.
Memory Recovery
Memory recovery is the process of retrieving memories that are there in the subconscious or unconscious mind but repressed or forgotten. In most cases, people undergo memory recovery therapy to deal with the pain and trauma associated with these memories.
The Link Between Memory Recovery And Repression Psychology
The link between memory recovery and repression psychology is simple. Repression is a defense mechanism to block traumatic memories from the person’s consciousness.
Now, in the process of memory recovery, we recover memories from repressed psychology. However, it is important to note that not everyone who experiences repression will remember their hidden memories.
The point of memory recovery is to regain control over one’s memories. This can be a very empowering experience, especially for people who have been through a traumatic event.
Memory Recovery As A Coping Mechanism
Memory recovery can also act as a coping mechanism for people who are struggling with the aftermath of a traumatic event. It can provide a sense of closure and allow people to move on with their lives.
If you have an interest in memory recovery, it is important to seek professional help. Many qualified therapists can assist you in retrieving your hidden memories.
Benefits of Memory Recovery

There are many benefits of memory recovery. Some of the key benefits include:
A sense of control over one’s life and memories: When memories are in the subconscious, it can feel like they are in control of us. However, recovering them gives back that sense of control.
Gaining a deeper understanding of oneself and one’s past: Often, recovering memories allows individuals to gain a deeper understanding of themselves and their past.
Closure and a feeling of moving on after a traumatic event: When a traumatic event happens, it can feel like life will never be the same again. Recovering memories can provide closure and allow individuals to move on with their lives.
Bringing peace of mind: Often, when memories are hidden, we spend a lot of time and energy trying to avoid them. Recovering them brings peace of mind and allows individuals to move on with their lives.
Improved mental health and well-being: Recovering memories can help people confront the emotions they have been repressing. This can lead to improved mental health and well-being.
Reduced symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): People who suffer from PTSD often have flashbacks and intrusive thoughts related to the traumatic event. Recovering memories can help reduce these symptoms.
Reducing stress and anxiety: When memories are repressed, they often cause a lot of stress and anxiety. Retrieving them allows individuals to deal with those feelings head-on.
Improved relationships: When people can confront the emotions related to a traumatic event, it can often improve their relationships with others.
Stages of Memory Recovery
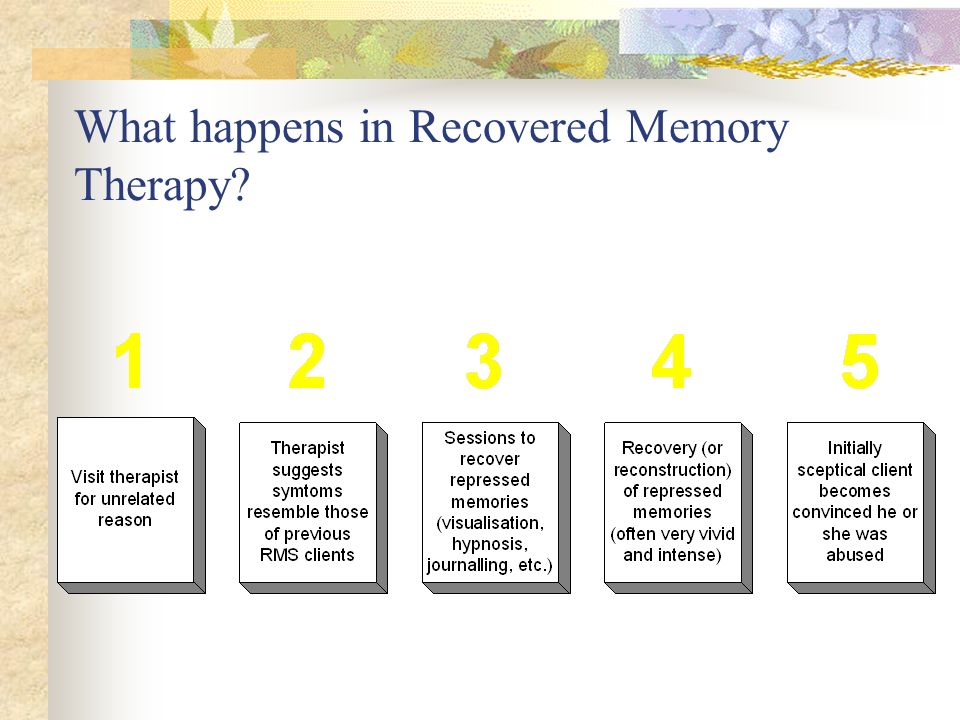
The process of memory recovery can be difficult but ultimately rewarding. There are typically four stages of memory recovery:
- Denial and Isolation: The person may deny that the event ever happened or they may isolate themselves from friends and family.
- Anger: The person may feel angry at themselves, the perpetrator, or God.
- Depression: The person may feel depressed and overwhelmed by the emotions they are experiencing.
- Acceptance: The person may eventually come to terms with the event and find a way to move on.
Each person experiences these stages in their unique way, and there is no set timeline for moving through them. It is important to remember that it is OKAY to take your time and progress at your own pace. There is no right or wrong way to deal with a traumatic event. Every person’s journey is different.
People Who Are Unfit For Memory Recovery
Some people are not fit for memory recovery. These include:
- People who have a history of mental illness,
- Those who are currently abusing drugs or alcohol, and
- Those who are not in a safe and healthy environment.
If you fall into any of these categories, it is best to wait until you are in a better place before you attempt to recover your memories.
How It Can Go Wrong
Memory recovery can go wrong if professionals don’t quite know the right technique. Several things can go wrong, including:
- Recovered memories may be inaccurate or false.
- Recovered memories may be disturbing or traumatic.
- The person may not be able to handle the emotions that came with the hidden memories.
False Memory Syndrome

False Memory Syndrome (FMS) is a condition that can occur after memory recovery therapy. FMS is characterized by the belief that memories of abuse or trauma have been created or implanted by the therapist.
NOTE: If you are considering memory recovery, it is important to be aware of False Memory Syndrome and the risks associated with it.
Risks Associated With False Memory Syndrome
There are several risks with False Memory Syndrome, including the person may:
- Become convinced that the memories are real, even if they are not.
- Start to doubt their sanity
- Experience anxiety or depression.
- Have difficulty trusting other people.
- Be unwilling or unable to continue with therapy.
Ways For Therapists To Avoid False Memory Syndrome
There are several ways that therapists can avoid False Memory Syndrome.
- First, they should only work with people who are mentally healthy and stable.
- Second, they should never force memories onto their patients.
- Third, they should always be supportive and non-judgmental.
- Fourth, they should encourage their patients to talk about their memories, even if they are painful.
Talking To A Professional
One should not attempt memory recovery without professional help. It is a complex process that professionals must conduct with diligence and care. Before you undergo memory recovery therapy, there are some things you need to take care of.
- First, make sure you are in a safe and healthy environment.
- Second, make sure you have a support system in place.
- Third, make sure you are ready to deal with the emotions that may come up during the therapy process.
Experts Opinion about Memory Recovery
There is a lot of debate surrounding memory recovery. Some experts believe that it is an effective way to deal with traumatic memories. While others believe that it can cause more harm than good.
Brain Activity During Memory Recovery
During memory recovery, the brain goes through several changes. Professionals can see/record it by measuring the brain’s electrical activity.
In a study conducted by Harvard University, researchers used MRI scans to track the brain activity of people who were recovering memories from repression psychology.
The results showed that the brain lit up in different areas depending on whether the memory was accurate or not.
HBOT (Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy)
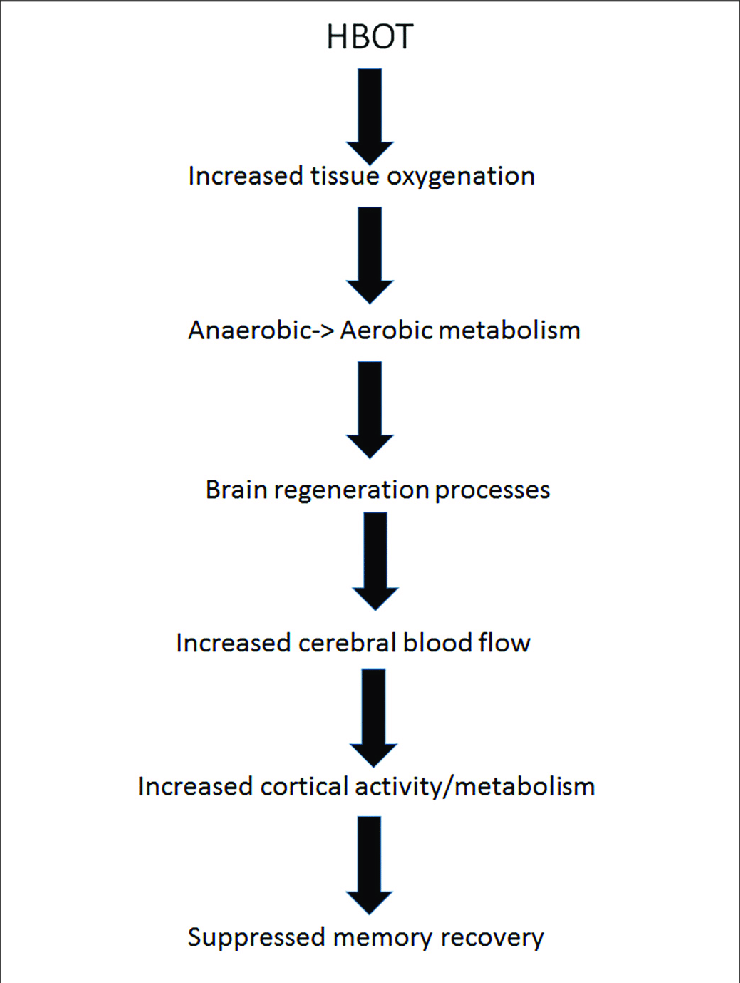
In some cases, people may choose to undergo HBOT or Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy. This is a type of therapy that involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized room.
HBOT has been shown to help people recover memories that have been repressed for years. It can also help reduce the symptoms of PTSD.
If you have an interest in HBOT, make sure to talk to your doctor about it. He or she may be able to refer you to a therapist who can help you get on it.
Case Study
The University of Southampton provides some insight into this question based on a case study. In the study, 19 participants had to recall a traumatic event from their childhood.
According to the results, when participants were to recall their memories, there was a change in their brain’s electrical activity. In particular, there was an increase in gamma activity. It shares a link with memory formation according to neurology.
Conclusion
The link between memory recovery and repression psychology is a complex one. But it is an important area of research. Memory recovery can be an empowering experience for people who have been through a traumatic event. It can also provide a sense of closure and allow people to move on with their lives.
However, it is important to remember that one must not attempt memory recovery without professional help. Several things can go wrong, including inaccurate memories or disturbing memories. It is also important to have a support system in place before undergoing therapy.
A Word From Therapy Mantra
Your mental health — Your psychological, emotional, and social well-being — has an impact on every aspect of your life. Positive mental health essentially allows you to effectively deal with life’s everyday challenges.
At TherapyMantra, we have a team of therapists who provide affordable online therapy to assist you with issues such as depression, anxiety, stress, workplace Issues, addiction, relationship, OCD, LGBTQ, and PTSD. You can book a free therapy or download our free Android or iOS app.


