Depressive disorders are a group of conditions that involve persistent feelings of sadness and/or hopelessness. They can range in severity, from minor symptoms that may go untreated to full-blown depressive episodes that can lead to serious problems. While there is no one type of depressive disorder, there are several types that share some common features. In this article, we’ll explore the different types of depressive disorders and their symptoms, as well as the treatments available for each.
Contents
- 1 What Are Depressive Disorders?
- 2 Different Types of Depressive Disorders
- 2.1 Major Depressive Disorder
- 2.2 Dysthymic Disorder
- 2.3 Bipolar Disorder
- 2.4 Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
- 2.5 Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
- 2.6 Situational Depression.
- 2.7 Psychotic Depression.
- 2.8 Peripartum (Postpartum) Depression
- 2.9 Persistent Depressive Disorder
- 2.10 Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD)
- 3 Common Signs of Depressive Disorders
- 3.1 Persistent Feelings of sadness or emptiness
- 3.2 Loss of Interest In Activities that used to bring joy
- 3.3 Changes In Appetite or Weight
- 3.4 Problems Sleeping
- 3.5 Fatigue or Decreased Energy
- 3.6 Difficulty Concentrating
- 3.7 Irritability or Restlessness
- 3.8 Feelings of Worthlessness or Guilt
- 3.9 Suicidal Thoughts or Attempts
- 4 Common Causes of Different Types of Depressive Disorders
- 5 Prevention of Depressive Disorders
- 6 Treatment of Different Types of Depressive Disorders
- 7 Conclusion
What Are Depressive Disorders?
 Defined to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV), a depressive disorder is characterized by a persistently sad, empty, or irritable mood, accompanied by somatic and cognitive changes that significantly affect a person’s capacity to function.
Defined to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV), a depressive disorder is characterized by a persistently sad, empty, or irritable mood, accompanied by somatic and cognitive changes that significantly affect a person’s capacity to function.
These disorders are the most common mental disorders in the world., affecting more than 15 million people, or about one in every five people.
Different Types of Depressive Disorders
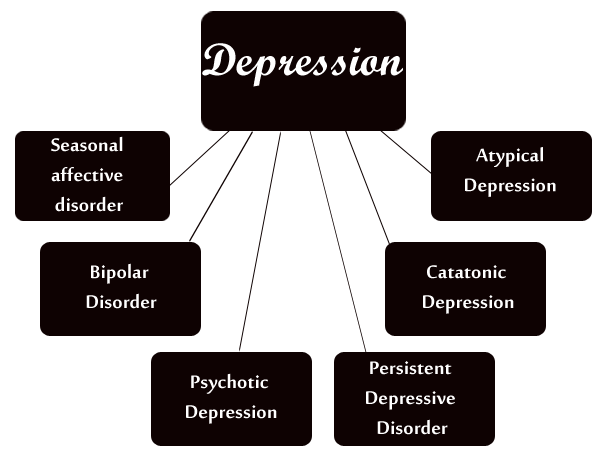
While there are many types of depressive disorders, they all share certain signs and symptoms. Different types of depressive disorders can be classified according to their severity, duration, and symptoms. The most common types of depressive disorders are major depression, dysthymia (persistent depressive disorder), bipolar disorder, seasonal affective disorder (SAD), postpartum depression, and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD).
Major Depressive Disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a mental disorder that is characterized by a persistent mood, decreased interest in activities, and poor self-esteem. It is the most common type of depression, affecting about 15 percent of the population at some point in their life. MDD can be classified into three types based on the cause of the depression: dysthymia, bipolar disorder, and unipolar major depressive disorder. There are several treatments available for MDD, including medication and psychotherapy. Psychotherapy can be effective if it is delivered by a qualified therapist who understands MDD and has experience treating it. Medication can help relieve symptoms of MDD, but it isn’t always effective and may have side effects.
If you are experiencing symptoms of MDD, please talk to your doctor or therapist about how to best manage them.
Dysthymic Disorder
Dysthymic disorder is a mental disorder characterized by a low mood, low energy, and apathy. It is the most common type of depressive disorder. The dysthymic disorder tends to occur more often in women than men. Symptoms typically first appear in late adolescence or early adulthood, but can also develop at any age.
Symptoms of dysthymia may fluctuate over time, which can make it difficult to identify the condition. Some common symptoms include:
- Weight gain or weight loss despite a healthy diet and regular exercise
- Insomnia or difficulty sleeping
- Low spirits or interest in activities that used to be enjoyable
- Changes in appetite, such as overeating or losing interest in food
- Racing thoughts, feelings of being overwhelmed, and trouble concentrating
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is a type of depressive disorder that includes two periods: mania (a period of intense happiness and energy) and depression (a period of decreased happiness and energy). Mania usually lasts for 2 to 4 weeks, and depression usually lasts for 6 to 12 months. Dysthymia is a type of depressive disorder that includes two periods: good days (a period during which you feel happy and energetic) and bad days (a period during which you feel sad and tired). Also, Dysthymia usually lasts for 6 to 12 months.
dysthymia is more common than either mania or depression, but it’s not as severe as either mania or depression. Dysthymia doesn’t
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can develop after a person experiences or witnesses a traumatic event, such as a car accident, violent crime, or sexual assault.
PTSD can cause intense anxiety and memories of the event to persist, even if the person no longer feels threatened. PTSD can also lead to problems with sleep, concentration, and mood.
There is no one-size-fits-all treatment for PTSD, but therapy and medication can help relieve symptoms.
Most people with PTSD recover fully, but it can take months or years to feel completely recovered.
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
 Seasonal Affective Disorder, or SAD, is a type of depressive disorder that occurs during winter. It’s typically diagnosed in people who experience major depressive episodes (moods that are so bad they interfere with daily life) during the fall and winter months. Symptoms of SAD include: fatigue, sadness, decreased energy, difficulty concentrating, weight gain, sleep problems, and thoughts of suicide.
Seasonal Affective Disorder, or SAD, is a type of depressive disorder that occurs during winter. It’s typically diagnosed in people who experience major depressive episodes (moods that are so bad they interfere with daily life) during the fall and winter months. Symptoms of SAD include: fatigue, sadness, decreased energy, difficulty concentrating, weight gain, sleep problems, and thoughts of suicide.
There isn’t one definitive answer to this question. However, experts believe that SAD is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some potential genetic factors that may play a role in the development of SAD include a history of depression or bipolar disorder in your family, being female, and being younger when you first experience symptoms of depression. Environmental factors that may contribute to the development of SAD include: living in an area with high levels of UV radiation (particularly in the fall and winter), experiencing a traumatic event (such as a death in the family), and having low levels of magnesium or zinc in your blood.
Situational Depression.
The most common type is situational depression, which occurs when a person’s mood changes in response to a life event or situation. Examples include being separated from a loved one or experiencing financial hardship. Other types of stressful situations that can lead to depressive symptoms include relationship problems, job layoffs, and physical illness.
Most depressive disorders can be treated with medication and therapy.
Psychotic Depression.
Characterized by negative thoughts and feelings, psychotic depression is a serious mental health condition. It’s often accompanied by hallucinations and delusions, which can make everyday activities difficult. Symptoms usually start after a traumatic event, such as a bereavement or a loss of a job. If left untreated, psychotic depression can lead to suicidal thoughts and actions.
There are three main types of psychotic depression: psychotic major, psychotic minor, and nonpsychotic depressive disorder. Psychotic major is the most severe form and is characterized by delusions that involve an out-of-control individual or group of people, such as persecution or being enslaved by aliens. Psychotic minor is less severe and usually involves more delusions that are focused on personal relationships or everyday life tasks. Nonpsychotic depressive disorder is the most common type of psychiatric disorder and involves persistent depressed mood without any delusions or hallucinations.
Peripartum (Postpartum) Depression
Peripartum depression is a type of depressive disorder that can occur during pregnancy or in the weeks or months following childbirth. It is thought to be caused by changes in hormone levels during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Symptoms of peripartum depression include feelings of sadness, anxiety, irritability, fatigue, difficulty sleeping, and difficulties with concentration and decision-making. Treatment for peripartum depression typically involves psychotherapy and/or antidepressant medication.
People usually feel better within a few weeks of starting treatment. If you think you might be suffering from peripartum depression, it is important to talk to your doctor or mental health professional as soon as possible.
Persistent Depressive Disorder
Persistent depressive disorder (PDD) is a serious mental illness that causes chronic, unrelenting sadness and hopelessness. PDD is one type of major depressive disorder. Symptoms of PDD typically persist for at least two years, although some people have the condition for much longer.
People with PDD often experience profound changes in their lives. They may lose interest in activities they once enjoyed, feel isolated from friends and family, and have trouble concentrating or making decisions. Some people with PDD also experience weight gain or loss, insomnia, and physical symptoms such as fatigue and headaches.
There is no known cure for PDD, but treatment options include medication and therapy. Medications used to treat PDD include antidepressant drugs such as Paxil, Prozac, and Zoloft. Therapy may include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or interpersonal therapy (IPT). Many people with PDD require both medication and therapy to achieve lasting improvement.
Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) is an umbrella term that includes a range of mood disorders that typically occur during the weeks leading up to or at the beginning of menstruation. These disorders include premenstrual syndrome (PMS), which is characterized by a variety of symptoms that typically worsen in the days before menstruation starts, and Premenstrual irritability syndrome (PIS), which is characterized by outbursts of anger, frustration, and anxiety.
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD)
Although PMDD is not officially recognized as a specific psychiatric disorder by some resources, it is now considered an important diagnosis when women experience symptoms that are not adequately explained by any other condition.
Common Signs of Depressive Disorders

There are many different types of depressive disorders, and each one has its own set of symptoms. However, some common signs may indicate that you or a loved one is suffering from a depressive disorder, such as:
Persistent Feelings of sadness or emptiness
This is one of the signs of Major Depressive Disorder (MDD), which is characterized by a persistently low mood that lasts for two weeks or more.
Loss of Interest In Activities that used to bring joy
If you used to enjoy going out with friends or participating in hobbies but no longer feel any pleasure in these activities, it could be a sign of depression.
Changes In Appetite or Weight
Depression can lead to changes in appetite and weight, either an increase or a decrease. For example, someone with depression may overeat and gain weight, or they may lose their appetite and become very thin.
Problems Sleeping
Insomnia is a common symptom of depression, which can make it hard to fall asleep or stay asleep. Depression can also cause excessive sleeping, known as hypersomnia.
Fatigue or Decreased Energy
Feeling tired all the time is a common sign of depression, even if you’re getting enough sleep. It can be hard to motivate yourself to do anything when you’re feeling this way.
Difficulty Concentrating
Depression can make it hard to focus on tasks or remember things. This symptom is often referred to as “brain fog.”
Irritability or Restlessness
People with depression may feel agitated or fidgety, and they may have difficulty sitting still for long periods.
Feelings of Worthlessness or Guilt
A person with depression may believe that they are not good enough or that they have done something wrong. These feelings can be intense and may lead to suicidal thoughts.
Suicidal Thoughts or Attempts
If you are having thoughts about harming yourself or taking your own life, this is a medical emergency and you should seek help immediately.
Common Causes of Different Types of Depressive Disorders
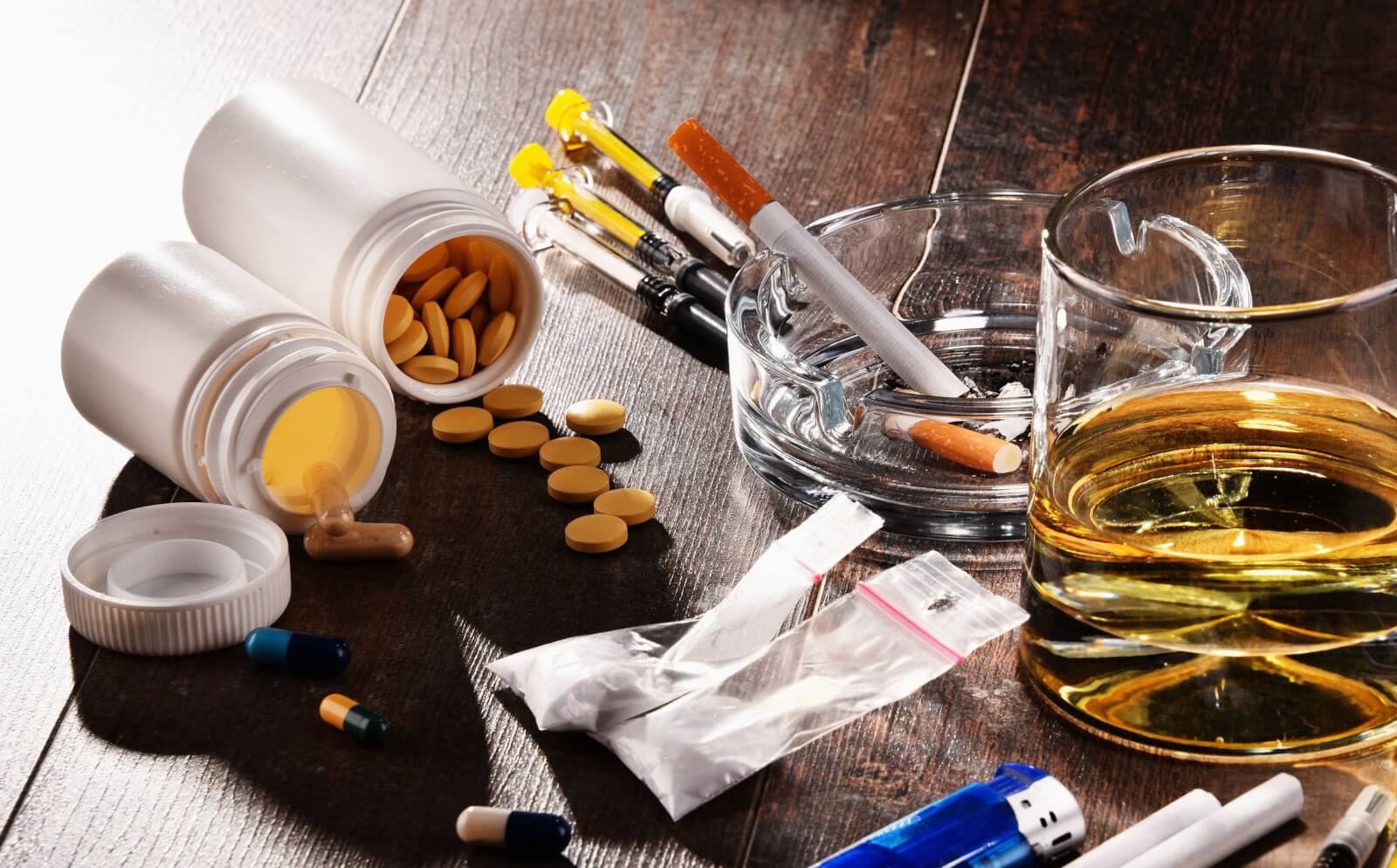
There are many different types of depressive disorders, and each type has its own set of symptoms and causes. While the exact cause of depression is not known, some common factors can contribute to the development of this condition. Some of these include
Genetic Predisposition
One of the main causes of depression is a person’s genetic makeup. If you have a family member who has suffered from depression, you are more likely to develop the condition yourself.
Brain Structure and Function
Another cause of depression is how the brain functions. People with depression often have changes in their brain structure and function, which can lead to a decrease in the level of neurotransmitters (chemicals that help relay messages between nerve cells). This can result in symptoms such as sadness, low energy, and difficulty concentrating.
Medical Conditions
Some medical conditions can lead to depression. These include thyroid problems, anemia, and certain types of cancer. Additionally, people who have chronic pain or other chronic illnesses may also be at risk for developing depression.
Substance Abuse
People who abuse alcohol or drugs are also more likely to develop depression. This is because substances can change how the brain functions, which can lead to a decrease in neurotransmitter levels and an increase in symptoms of depression.
Stressful life events
Life events such as the death of a loved one, divorce, or job loss can also lead to depression. This is because these events can be very stressful and can cause a person to feel hopeless and helpless. Additionally, people who have experienced trauma may also be at risk for developing depression.
While there are many different causes of different types of depressive disorders, these are some of the most common. If you think you may be suffering from this condition, it is important to the essential doctor so that you can get the help you need.
Prevention of Depressive Disorders
Depression is a serious mental illness that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Although there is no one way to prevent depression, there are many effective steps that you can take to reduce your risk of developing the condition.
Here are some tips for the prevention of depressive disorders
1. Get enough sleep. Enough sleep is key for overall health, but it is especially important for preventing depression. Insufficient sleep may lead to increased levels of stress and anxiety, which can in turn lead to depression. Get at least seven hours of sleep each night.
2. Eat a healthy diet. A healthy diet can help improve overall mood and happiness, as well as prevent depression. Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat foods to boost your intake of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Limit sugar and processed foods, which have been linked with an increased risk of depression.
3. Exercise regularly. Exercise has many mental health benefits, including reducing anxiety and stress levels. Physical activity has also been shown to help treat depression symptoms such as feelings of hopelessness and sadness. Aim to get at least 30 minutes of exercise every day.
4. Connect with friends and family members. Social support is key for preventing and managing depression. Make time for friends and family members, whether it’s by going out for coffee or watching a movie together.
5. Seek professional help if needed. If you experience signs of depression, such as feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or decreased energy, talk to your doctor about your situation. A mental health professional can help you determine the best course of action for treating your depression.
Treatment of Different Types of Depressive Disorders
 Treating a depressive disorder can be tricky, and it often requires a combination of different types of treatment. The most common type of treatment for depression is medication, which can be prescribed by a psychiatrist or other mental health professional. Medication can be very effective in treating the symptoms of depression, but it is important to remember that it is not a cure. In addition to medication, therapy is also an important part of treatment for many people with depression.
Treating a depressive disorder can be tricky, and it often requires a combination of different types of treatment. The most common type of treatment for depression is medication, which can be prescribed by a psychiatrist or other mental health professional. Medication can be very effective in treating the symptoms of depression, but it is important to remember that it is not a cure. In addition to medication, therapy is also an important part of treatment for many people with depression.
Therapy can help you understand your thoughts and feelings, and learn how to cope with them healthily. It can also provide support and guidance as you work through difficult life situations. If you are considering therapy, make sure to find a therapist who is experienced in treating depression and to who you feel comfortable talking.
In addition to medication and therapy, there are several other things you can do to help manage your depression. Getting regular exercise, eating a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and avoiding alcohol and drugs can all help reduce the symptoms of depression. If you are having difficulty managing your depression on your own, don’t hesitate to reach out for help from a friend or family member. There are also many helplines and support groups available, which can provide valuable information and support. Remember, you are not alone in this – there is help available if you need it.
Conclusion
Depressive disorders are a heterogeneous group of disorders. The different types of depressive disorders share certain features, but also have important differences.
If you think you may be suffering from a depressive disorder, it is important to seek professional help. A mental health professional can conduct a thorough evaluation and make a diagnosis. Once the diagnosis is made, the mental health professional can develop a treatment plan that is tailored to your specific needs. If you are struggling with depression, know that you are not alone and there is help available. Seek out a mental health professional today and start on the road to recovery.
Hope this article was of help to you! If you are suffering from depressive disorders, you may seek help from Therapy Mantra. We have a team of highly trained and experienced therapists who can provide you with the tools and skills necessary for overcoming depressive disorders. Contact us today to schedule an online therapy or download our free Android or iOS app for more information.


