If you’ve ever been afraid of something that didn’t make sense, then you have irrational fears. Irrational fears are a type of phobia and can be very disabling for those who suffer from them.
In this blog post, we will discuss the types of irrational fear, how they affect people, what causes them to develop, and treatment options available to help get rid of your fear once and for all!
Contents
Understanding Irrational Fears Or Phobia

To understand irrational fears, you first need to understand the difference between “normal” fears and phobias or “irrational” fears. Normal fears are a natural response to something that we perceive as dangerous or threatening. For example, the fear of spiders is considered normal because most people see spiders as being harmful.
Phobias (irrational fears) are an intense or irrational fear of something that doesn’t pose a threat. For example, you may be afraid to leave your house because you’re terrified about the possibility of having a panic attack in public and it’s this feeling that makes going outside impossible for some sufferers.
Psychology Of Irrational Fears
Irrational fears can develop in our brains for any number of reasons. Most often, irrational fears are the result of classical conditioning. This is when we come to associate certain things with negative feelings or experiences and it causes us to fear something that doesn’t pose a threat.
For example, if you were mugged at gunpoint on your way to work in the morning, you might develop a fear of going outside. Or if your dog was run over by a car when he chased after it one day, then this event could cause him to be fearful of cars for life – even though they pose no threat now.
Symptoms Of Irrational Fears
Irrational fears can cause a lot of distress and anxiety for those who suffer from them. Some common symptoms include:
- Racing heart
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating
- Trembling or shaking
- Feeling lightheaded or dizzy
- Nausea
- Difficulty concentrating
Causes Of Irrational Fears
There is no one-size-fits-all cause of irrational fears. However, there are some common causes including:
- Uncontrollable/unpredictable thoughts
- Genetics or hereditary factors
- Negative past experiences (e.g., a traumatic event)
- Lack of self-confidence and feeling helpless to cope with anxiety symptoms in general
Degrees Of Irrational Fears
There are different degrees of irrational fears. Some people may only experience a mild fear of something, while others may have an intense and paralyzing fear. The degree of fear can also vary depending on the person’s environment and what they’re afraid of. For example, someone who has a fear of flying may only experience a mild fear when they’re on a plane, but they may have a panic attack if they’re at the airport.
Irrational Fears And Mental Health
Irrational fears and mental health do not always go hand in hand. However, the level of anxiety that comes with irrational fears can often lead to other types of mental disorders such as:
- Depression
- Anxiety disorder
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Social phobia or social anxiety disorder
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
Irrational fears can also be a sign that something else is going on with your mental health. If you’re experiencing irrational fears and other symptoms of anxiety, it’s important to seek professional help.
Types Of Irrational Fears
Different types of irrational fears can affect people of all ages. Some common examples include:
In Children
- Animal phobias (e.g., spiders, snakes)
- Natural environment phobias (e.g., thunderstorms, heights)
- Social phobia (fear of crowded places and social situations like public speaking or eating in front of others)
- Specific phobias such as acrophobia (fear of heights), claustrophobia (fear of small spaces), and aerophobia (fear of flying).
In Adults
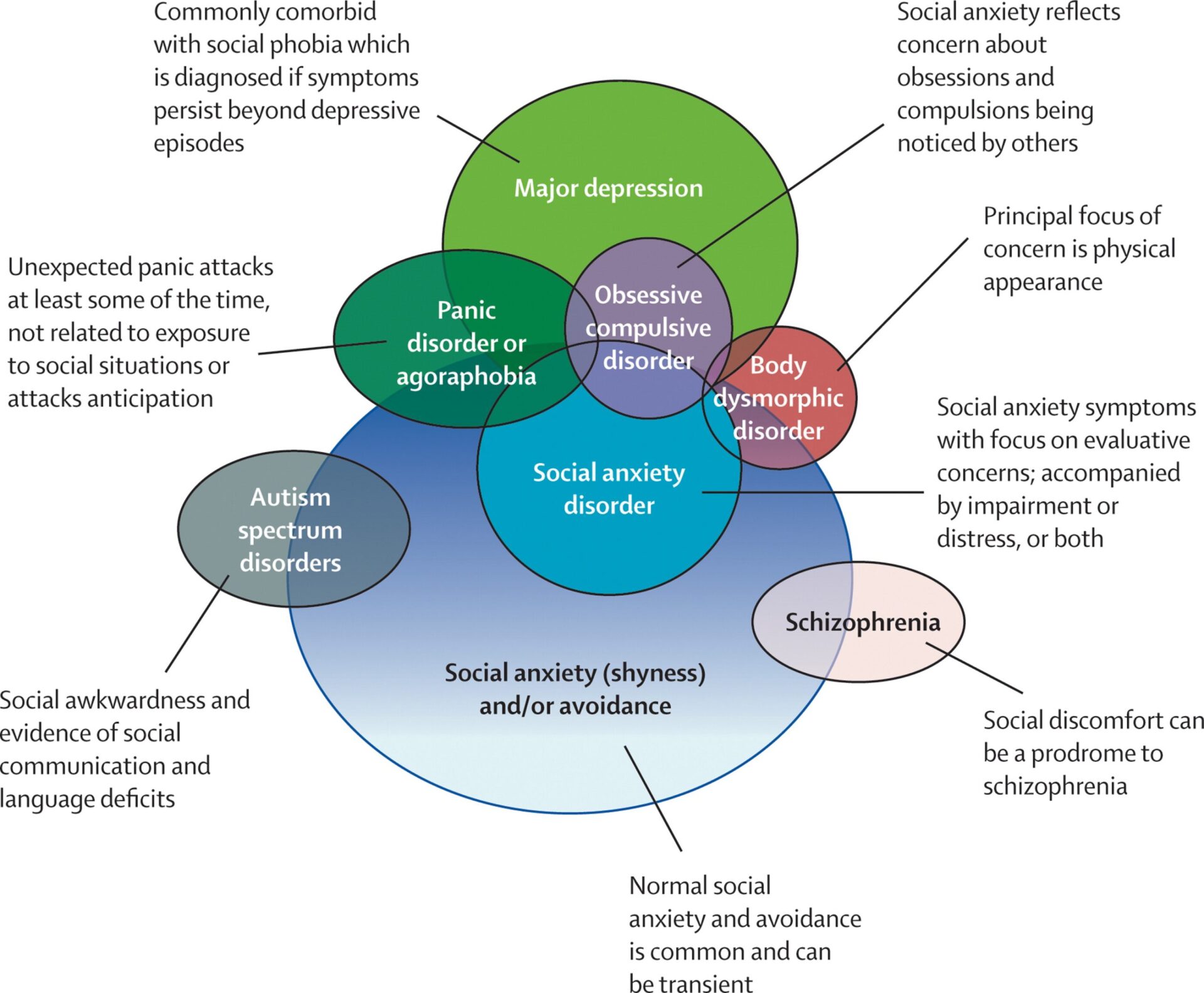
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
A condition where a person has intrusive thoughts that they can’t get rid of and feels the need to perform certain rituals or routines to relieve their anxiety. It results in irrational fears of contamination, harm, or orderliness.
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
A condition that can develop after a person experiences a traumatic event such as a car accident, sexual assault, war, or natural disaster. People with PTSD may experience flashbacks, nightmares, and intrusive thoughts about the event.
Social anxiety disorder (SAD)
A condition where a person has an excessive and irrational fear of social situations. They may feel uncomfortable meeting new people, talking in front of groups, or eating in public.
Specific phobias
A condition where a person has an irrational fear of something they consider dangerous or harmful. Common examples include:
- Acrophobia (fear of heights),
- Claustrophobia (fear of small spaces),
- Agoraphobia (fear of crowded places).
In Senior Citizens
Alzheimer’s disease
A progressive brain disease that leads to a decline in memory and intellectual abilities. As the disease progresses, people may experience changes in mood and behavior, including becoming fearful or paranoid.
Dementia
A condition that results in the loss of intellectual abilities and skills such as memory, thinking, and reasoning. It can sometimes lead to irrational fears about personal safety or being left alone.
Caregiver burnout
This is when caregivers (usually family members) have intense feelings of physical, emotional, and mental exhaustion due to the demands of caring for someone with dementia. This can lead to irrational fears about being able to care for the person in the future.
“Normal” Fears Vs. Phobias Or “Irrational” Fears
It can be tricky to determine whether fear is considered normal or irrational. However, there are some key differences between the two:
- Normal fears happen in response to something that we see as a threat and they’re usually based on reality. For example, the fear of spiders is considered normal because most people know that spiders can be dangerous.
- Irrational fears are intense and persistent, even though they’re not based on reality or fact. For example, the fear of flying is irrational because airplanes are very safe modes of transportation.
Dealing With Irrational Fears Or Phobia

Self-Help Tips
Some self-help tips can be useful for those who suffer from irrational fears or phobias. Some of these tips include:
Identifying your fear
This can help you to understand why the fear is causing so much distress and what might trigger it.
Challenging your thoughts
When you have fearful thoughts, try to identify the negative thought. Then, think of a contrary example that challenges your initial thoughts
Creating new routines
If you have trouble doing something because it triggers an irrational fear or phobia, creates some small steps toward completing this task until you can do it again without any distress.
Treatment Options For Irrational Fears Or Phobias
Several treatment options are available for those who suffer from irrational fears or phobias. Some common treatments include:
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
This type of therapy helps people to change the way they think about and react to their fear triggers. It can help to reduce the anxiety and panic that is associated with these triggers
Exposure therapy
This type of therapy involves gradually exposing a person to the fear trigger in a safe and controlled environment. This can help them to learn how to cope with their fear.
Medication
Several medications can be prescribed to help reduce anxiety symptoms. This includes antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, and beta-blockers.
Talking To A Professional
If dealing with irrational fears on your own is too difficult, it may be a good idea to seek professional help. A therapist can teach you more about your fear and how to cope with anxiety symptoms in general so that they don’t get out of control again. In some cases, medication may also be needed if the person’s phobia is severe.
Expert Comments On Irrational Fears
Many experts agree that the best way to treat irrational fears is through cognitive-behavioral therapy. This involves working with a therapist or counselor who can help you learn how to control your fear, break free from avoidance behaviors, and face what you’re afraid of. Some therapists use exposure techniques in their sessions by having clients gradually relax while thinking about or being in contact with the fear until it becomes less frightening.
Case Study
Here is an example of how CBT was able to help a woman with a fear of spiders:

The therapist started by having the client keep a journal in which she wrote down her thoughts and feelings about spiders. The therapist then asked the client to identify her beliefs about spiders. The client believed that all spiders were dangerous, they would bite her, and she would die from the venom.
The therapist helped the client to realize that these beliefs were not entirely true nor rational. For example, spiders do not always bite humans even though they can be dangerous if provoked or threatened; many people are bitten by a spider but survive, and there is an antivenom for those who do get bitten by a spider.
The therapist then helped the client to come up with new, more rational beliefs about spiders such as “spiders can be dangerous but I can take precautions to stay safe” and “I may not like spiders but they are important for our environment.”
With these new beliefs in place, the therapist worked on exposure techniques with the client. They started by reading an article about spiders together and then moved on to looking at a picture of a spider through half-closed eyes while imagining it crawling toward them, and eventually building up to watching videos of spiders in nature.
Each exposure session was followed by positive self-talk for coping with any resulting anxiety or fear. After a few months of therapy, the client was able to approach spiders without fear or anxiety and even touch them if they were in a controlled setting.
Conclusion
Irrational fears can be extremely frustrating and stop you from living a normal life. However, there is help out there and it’s important to remember that fears are normal – we all have them at one time or another. The difference between a phobia and a fear is how intense it feels for the person experiencing it. There are different treatment options available depending on what type of irrational fear you’re struggling with: self-help tips, therapy, or medication. Seeking help is the most important thing you can do if irrational fears are telling you to stop living your life. Last but not least, keep reminding yourself that they are not real!
A Word From Therapy Mantra
Your mental health — Your psychological, emotional, and social well-being — has an impact on every aspect of your life. Positive mental health essentially allows you to effectively deal with life’s everyday challenges.
At TherapyMantra, we have a team of therapists who provide affordable online therapy to assist you with issues such as depression, anxiety, stress, workplace Issues, addiction, relationship, OCD, LGBTQ, and PTSD. You can book a free therapy or download our free Android or iOS app.


