Do you suffer from OCD? If so, you may be interested in deep brain stimulation (DBS). DBS is a surgical procedure that involves implanting electrodes into the brain. This procedure is used to treat a variety of medical conditions, including OCD. In this guide, we will discuss everything you need to know about DBS for OCD. We will cover topics such as eligibility, risks and benefits, and the surgery itself. We hope this guide provides you with all the information you need to make an informed decision about deep brain stimulation for OCD.
Contents
Defining Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation, so popular by the acronym DBS, is a surgical procedure in which electrical impulses are delivered to specific areas of the brain. This treatment is used for a variety of conditions, including Parkinson’s disease, dystonia, and essential tremor. DBS for OCD is approved by the FDA as an investigational device, which means that it is still being studied and has not yet been proven effective for this condition.
This is a surgical procedure administered by a qualified surgeon. The goal of DBS for OCD is to modulate the activity of specific areas of the brain that are thought to be involved in the development and maintenance of OCD symptoms. This treatment is considered to be investigational, which means that there is still some uncertainty about its efficacy and long-term risks.
How Does It Help OCD?
The procedure for DBS for OCD is similar to that for other conditions. The surgery involves the implantation of electrodes in specific areas of the brain. These electrodes are connected to a device called a pulse generator, which is implanted under the skin of the chest, nearby the collarbone. The pulse generator delivers electrical impulses to the electrodes, which modulate the activity of the brain regions that they target.
After surgery, the patient works with a team of doctors, nurses, and therapists to learn how to use the device. The pulse generator is programmed to deliver electrical impulses to specific areas of the brain. These impulses are thought to help modulate the activity of brain circuits that are involved in the development and maintenance of OCD symptoms. It also contributes to the long-term safety and efficacy of the treatment.
It is thought that DBS for OCD may help to reduce symptoms by modulating the activity of brain circuits involved in the development and maintenance of OCD. However, this treatment is still being studied and has not yet been proven effective for treating OCD.
A surgical route such as DSB is a great recommendation for mental illnesses like OCD as it is helpful in modulating the activity of certain areas in the brain. This can prove to be helpful in the long run as it is more durable and has a lower risk for potential side effects.
If you or someone you know is struggling with OCD, deep brain stimulation may be an option worth considering. DBS is still being studied and has not yet been proven effective for treating OCD, but it is a promising treatment option for those who are struggling to find relief from their symptoms.
Who Should Consider?
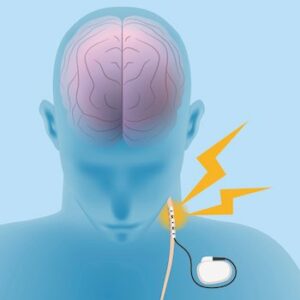
The eligibility for who can undergo deep brain stimulation for OCD is a tricky question as the treatment is still investigational. This is because the long-term risks and benefits of the treatment are not yet known.
That being said, DBS for OCD is typically reserved for patients who have failed to respond to other treatment options, such as medication and cognitive-behavioral therapy.
It can also be an option for patients who are unable to tolerate the side effects of other treatments, or for whom other treatments have proven to be ineffective.
In some cases, your therapist may also recommend DBS for OCD if they feel that you would benefit from the treatment. This is for when the traditional and conventional methods are unable to manage symptoms or your disorder is caused by any physiological or biological reasons.
Who Should Avoid?
Now that we know who the surgery is for, it is also important to know who should avoid the surgery. The risks and benefits of DBS for OCD are still being studied, so it is important to talk to your doctor about whether or not the treatment is right for you.
That being said, there are some people who should avoid DBS for OCD, such as:
- People with active substance abuse disorders
- Pregnant or lactating people
- People with certain medical conditions, such as bleeding disorders or a history of strokes
- People with certain mental disorders, such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder
DBS for OCD is a promising treatment option, however, it is important to pay attention to the risks and benefits before making a decision. Be sure to talk to your doctor about whether or not DBS for OCD is right for you.
What To Expect?
Surgery can be an overwhelming, and even scary, experience. It is important to know what to expect before undergoing any type of surgery.
DBS for OCD is a minimally invasive surgery, which means that it is a less invasive alternative to traditional brain surgery. The risks and side effects of DBS are typically milder than those of traditional brain surgery.
Before Surgery
The whole procedure of surgery begins with a consultation. During the consultation, the doctor will assess your symptoms and medical history to see if DBS for OCD is right for you.
They will also answer any questions that you may have about the surgery. Once you have decided to undergo DBS for OCD, the next step is to schedule the surgery.
The surgery itself is typically done as an outpatient procedure, which means that you will be able to go home the same day as the surgery. One may also need a valid and verified surgery date, which is given by the hospital.
During Surgery
The surgery itself takes about two to three hours. During the surgery, your surgeon will make a small opening in your skull. They will then insert a thin, flexible wire into your brain. This wire is connected to a battery-operated device that will be placed under the skin of your chest. Since patients are under general anesthesia during the surgery, they will not feel any pain.
Another thing that happens during surgery is that your surgeon will test the wire to make sure it’s in the right spot. They do this by sending electrical signals through the wire. If everything is working correctly, you should feel a temporary change in your symptoms.
The device sends electrical signals to specific areas of your brain that are thought to be involved in OCD. Some researchers believe that it may help normalize brain activity. The device is usually turned on a few weeks after surgery, once you have recovered from the procedure.
After Surgery
After the surgery, you will need to stay in the hospital for a few days. During this time, your doctors will closely monitor you for any side effects.
After you regain consciousness, your respective doctor will talk to you about your experience. You may feel some side effects, such as headache, confusion, or dizziness. These side effects are usually temporary and should go away within a few days.
They will also teach you about how to care for your device and what to do if you have any problems. It is important to follow their instructions carefully.
The risks that come after this procedure are usually low and can be minimized by working with a qualified and experienced surgeon.
It is important to follow up with your doctor after surgery. They will need to check on your progress and see how you are responding to the treatment.
Some things to remember about deep brain stimulation:
- The device is NOT a pacemaker. It will not regulate your heartbeat.
- Batteries in the device will need to be replaced every few years.
- The device can be turned off at any time if you no longer want to receive the treatment.
The aftermaths are as crucial as the surgery itself. One must take care of themselves and follow the doctor’s orders to ensure a speedy recovery.
Benefits
DBS for OCD is a promising treatment option for OCD along with other neurological disorders. It has an array of benefits such as:
- It is minimally invasive: The surgical procedure for DBS is minimally invasive, which means that it causes minimal damage to the brain.
- It is reversible: If a patient decides that they no longer want to receive DBS for OCD, the surgeon can remove the electrodes and pulse generator. In cases wherein the patient has a need for long-term treatment, the battery can be replaced through a minor surgical procedure.
- It is adjustable: The electrical impulses delivered by the pulse generator can be adjusted to meet the needs of the individual patient. This means that the treatment can be customized to each person’s unique situation. The surgeon can adjust the settings of the device to target different areas of the brain or to change the intensity of the electrical impulses.
- It is safe: DBS for OCD is considered to be a safe treatment option. The risks associated with the surgery are low, and the majority of patients who receive DBS for OCD experience no serious side effects.
- It does not damage brain tissue: Unlike some other surgical procedures for OCD, DBS does not damage brain tissue. Rather, it modulates the activity of specific areas of the brain.
- It is covered by insurance: Lastly, the advantage of the surgery cost being covered by insurance is that it is widely available to patients who need it.
With all of these advantages in place, deep brain stimulation becomes an effective and highly recommended treatment option for OCD.
Risks
As with any surgical procedure, there are risks associated with DBS for OCD. These risks include:
- Infection
- Bleeding in the brain
- Stroke
- Seizures
- Nerve damage
- Changes in mood or behavior
There is also a risk that the electrodes will move out of place after surgery. In some cases, this may require another surgical procedure to fix the problem. Risks specific to DBS for OCD can also include worsening OCD symptoms, as well as depression and anxiety.
DBS is not a cure for OCD, and it is possible that symptoms may worsen after surgery. It is important to discuss all potential risks and benefits of this treatment with a qualified surgeon before making the decision to undergo the procedure.
Recovery And Precautions
Since DBS is a minimally invasive surgery, the recovery time is usually short. Most people are able to go home the same day or the day after surgery. It is important to follow all of your surgeon’s instructions for recovery, which may include taking antibiotics to reduce the risk of infection and avoiding strenuous activity for a period of time.
There are some precautions one might want to keep in mind to avoid any complications or risks. These include:

- Do not drink alcohol or use recreational drugs for at least 24 hours after the surgery
- Do not drive or operate heavy machinery or operating power tools
- Avoid any contact sports or ones that require wearing a helmet
- It is also important to keep the surgical site clean and dry. You should avoid taking baths or swimming until your surgeon gives you the green light.
It is also important to keep in mind that DBS for OCD is not a cure, and symptoms may worsen after surgery. It is important to discuss all potential risks and benefits of this treatment with a qualified surgeon before making the decision to undergo the procedure.
Alternative Methods
If deep brain stimulation for OCD is something you are unsure about, don’t worry! There are many other treatment options available that may be more suitable for you. Some of these include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: This type of therapy focuses on changing the thoughts and behaviors that contribute to OCD.
- Exposure and Response Prevention Therapy: This therapy involves gradually exposing yourself to the things that trigger your OCD while practicing ways to prevent compulsions from taking over.
- Medications: Medications such as antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications can be effective in treating OCD.
- Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT): ECT is a treatment that uses electrical currents to induce seizures in the brain. It helps by resetting the brain’s circuitry and has been shown to be effective in treating OCD.
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS): TMS is a treatment that uses magnetic fields to stimulate the brain. It is a non-invasive and relatively new treatment option that is showing promise in treating OCD.
- Natural treatments: There are also a variety of natural treatments that can be effective in treating OCD. These include methods such as:
-Herbal supplements
-Acupuncture
-Yoga
-Hypnosis
-Meditation
While deep brain stimulation for OCD may be an effective treatment option, it is not right for everyone. Surgery is not the only treatment option available for OCD, and it is important to discuss all of your options with a qualified mental health professional before making any decisions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, deep brain stimulation for OCD is a minimally invasive surgery that can be an effective treatment option for some people. It is important to discuss all potential risks and benefits of this treatment with your respective healthcare provider. Deep brain stimulation for OCD is a highly effective and widely available treatment option. However, it is not right for everyone. Be sure to talk to your doctor about all of your options before making a decision on which treatment is best for you. There are a variety of alternates available if this isn’t the most suitable option for you.
If you or someone you know suffers from OCD, you may consider Therapy Mantra for assistance. We have a team of highly qualified mental health professionals who can provide you with the treatment and support you need. Contact us today to book an online therapy session or download our free OCD treatment app on Android or iOS for more information.